The Skeletal System
advertisement

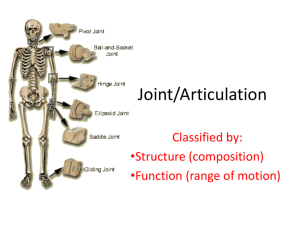
The Skeletal System Articulations Classification Classified based on the type of movement they allow. 3 major types: Fibrous Joint – immovable and connected by fibrous connective tissue (ex: plates in skull, periodontal ligaments) Cartilaginous Joint – slight movement and fibrocartilage is between the 2 bones (ex: betw. spinal vertebrae & pubic bones) Synovial Joint – free motion no direct contact of bones associated with synovial membranes (Ex: elbow, ankle, shoulder) Fibrous Joints: minimal movement Sutures: seams between bones, found between skull bones, form fontanels in children (e.g. coronal) Syndesmoses: bones farther apart than in a suture and are joined by ligaments (e.g. radioulnar) Gomphoses: specialized joints consisting of pegs that fit in sockets (e.g. dentoaveolar) Cartilaginous Joints: Growth Synchondroses: 2 bones joined by hyaline cartilage (e.g. epiphyseal platescartilaginous region betw. epiphysis & diaphysis of a growing bone) Symphyses: fibrocartilage uniting 2 bones (e.g. symphyses pubis, manubriosternal (ribcage)) Synovial Joints: Movable Plane or gliding: 2 opposed flat surfaces, movement confined to one plane (e.g. intervertebral) Saddle: 2 saddle-shaped articulating surfaces oriented at right angles (e.g. carpometacarpel- wrist/hand) Hinge: convex cylinder in one bone applied to a corresponding concave portion on another bone (e.g. elbow and knee) Pivot: rotation around a single axis. A process that rotates within a ring (e.g. atlantoaxial-neck) Synovial Joints Ball and Socket: ball (head) at the end of one bone and a socket on another bone (e.g. coxal-hip and glenohumeralshoulder) Ellipsoid: modified ball-and-socket the head is more ellipsoid in shape rather than round (e.g. atlanooccipitalbetw.head & neck i.e. allows nodding) Types Movements Flexion (anterior or ventral direction) and extension (posterior or dorsal direction) Dorsiflexion (flex toes) and plantar flexion (point toes) Abduction (away from midline) and adduction (toward midline) Medial and lateral rotation (turning around long axis) Circumduction (combination of flexion, extension, abduction, and adduction) Elevation (superior motion) and depression (inferior motion) Protraction (moving in anterior direction) and retraction (moving in posterior direction) Supination (face up palm) and pronation (face down palm) Opposition (thumb to finger) and reposition Lateral excursion (bottom jaw lateral) Inversion (ankle medial turn) and eversion (ankle lateral turn)