skeleton - Macmillan Academy
advertisement

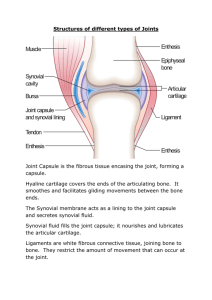
SKELETON 4 Functions of Skeleton and key points / examples JOINTS 3 Types of joints and their characteristics JOINTS 5 types of Synovial Joints Protection of vital organs e.g. skull – brain, ribs – heart and lungs Shape and Support – Provide frame for all of body Blood Production – Bone marrow produces red blood cells Movement – Muscles are attached to bones - Bones form joints 1) Fixed / Immovable – e.g. Cranium – Lots of small piece of bone joined together – they do NOT move 2) Slightly Movable – e.g. Vertebrae – Small amount of movement but quite stable 3) Freely Moveable / Synovial – e.g. shoulder, knee, hip Gliding – e.g. tarsals and carpals Hinge – e.g. knee, elbow Pivot – e.g. neck Ball and Socket – e.g. shoulder, hip Saddle – e.g. thumb CONNECTIVE TISSUES 1) Tendons – connect muscle to bone What are the 3 types and what do they do? 2) Ligaments – connect bone to bone 3) Cartilage – covers the end of bones at a joint to prevent friction