File
advertisement

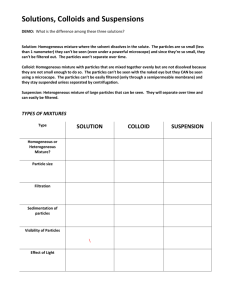
Chapter 12.1 Notes 8R Types of Mixtures Homogeneous- uniform throughout (at molecular level) Heterogeneous- not uniform Organize the following mixtures as homogeneous or heterogeneous. Homogeneous Heterogeneous Lucky charms cereal Sterling silver Orange juice (with pulp) Air (in the classroom) Air filled with smoke Milk Sugar water Clay and water mixed Ocean water I. Solutions Soluble-capable of being dissolved ____________ is an example that is insoluble in water. Solution- a homogeneous mixture of two or more substances in a single phase. Atoms, molecules, or ions are thoroughly mixed; the mixture has the same composition throughout. A. Components of Solutions Solvent- dissolving medium; the component with greater quantity. Solute- substance being dissolved; the one w/ lesser amount B. Types of Solutions Look at Table 1. Name the solvent and the solute. Mixture solvent solute water sugar, salt, colors, Gatorade preservatives water fat, Ca, sugar milk water CO2, HFCS, color, soda acid O2 air (in the class) N2 Au Ag, Cu 14-karat gold water ethanol, sugar Wine II. Suspensions Suspension- a type of mixture in which the particles settle out when it’s no longer stirred. Examples: oil and water, mud and water, ketchup III. Colloids Colloid- a mixture in which particles are intermediate in size between those in solutions and suspensions. The particles are larger than those in a solution but they stay mixed. Examples: Look at the examples in Table 2 on pg 404. Write three examples in your notes. A. Tyndall Effect The Tyndall Effect occurs when light is scattered by colloidal particles. Example: when you can see a headlight beam from the side on a foggy night. IV. Solutes: Electrolytes vs. Nonelectrolytes Electrolyte – a substance that dissolves in water to give a solution that conducts electricity. = Ionic. Nonelectrolyte - a substance that dissolves in water to give a solution that does not conduct electricity. = Covalent. Examples: NaCl – is an electrolyte because it’s ionic Sucrose – is a nonelectrolyte because it’s covalent HW: Section 12.1 Review # 1-6 on page 406