Particle Theory/Chemical
advertisement

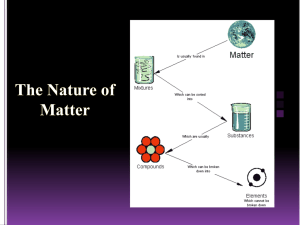
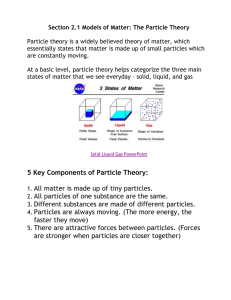
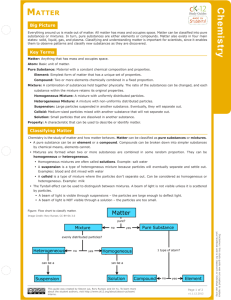
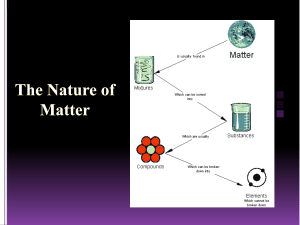
The Particle Theory of Matter All matter is made up of extremely tiny particles. Each pure substance has its own kind of particle, different from the particles of other pure substances. Particles attract each other. Particles are always moving. Particles at a higher temperature move faster on average than particles at a lower temperature. Copy figure 5.1A, 5.1B, and 5.1C into your notebooks Define each of the following terms: scientific model, heterogeneous, homogeneous, solution, mechanical mixture, qualitative physical property, and quantitative physical property Scientific model: scientific models are used to help scientists to picture, in an imaginative way, processes in nature that cannot simply or directly be seen. Example: The particle theory of matter. Heterogeneous: is a term applied to mixtures that are not found of a uniform composition throughout. It is an uneven mixture that contains two or more substances. Homogeneous: a term applied to pure substances and to mixtures that are of a uniform composition throughout. It is a mixture that is the same throughout. Solution: a homogeneous mixture of two or more pure substances. Mechanical Mixture: a heterogeneous mixture where at least two substances are visible. Qualitative physical property: a characteristic of a substance that can be described but not measured. Examples: smell, state, taste, texture. Quantitative physical property: a characteristic of a substance that can be measured. Examples: density, melting temperature, boiling temperature. Chemical or Physical Changes/Properties Physical Change is a change in matter in which no new substance is formed. Examples: melting, density, volume, mass, boiling, freezing, and evaporating. Any property that can be observed or measured without forming a new substance is a physical property. Color and density are examples of physical properties. Color can be observed without touching or changing, density is the amount of matter that occupies a certain space. Density can be measured without forming a new substance so density is also a physical property. Chemical Change is a change in matter in which at least one new substance, with new properties, is formed. Example: heat or light is given off (burning), bubbles form, a new color appears, change is not easily reversible, and a precipitate (solid material) forms in a liquid. Any property that describes how a substance reacts with another substance when forming a new substance is called a chemical property. Combustibility is the ability of a substance to burn in air and is therefore a chemical property.