File
advertisement
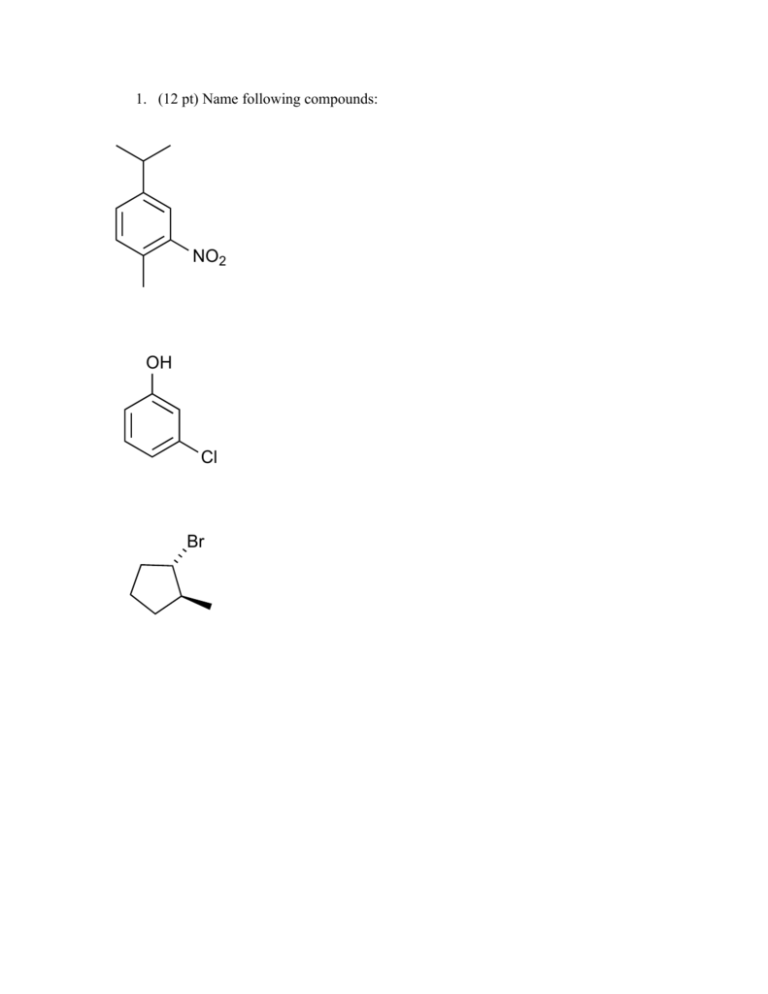
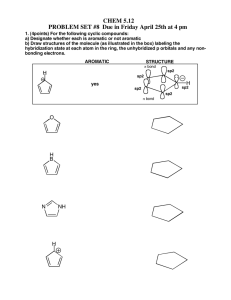
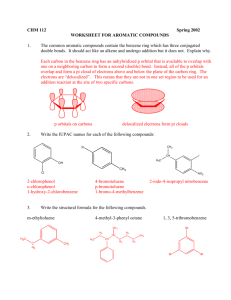
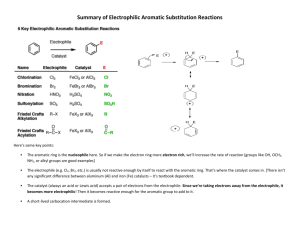
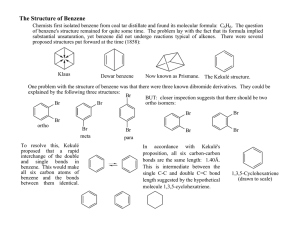
1. (12 pt) Name following compounds: NO2 OH Cl Br 2. (9 pt) Draw the following compounds. a. benzyl bromide b. 3,5-dimethylaniline c. (S)-2-chlorobutane 3. (8 pt) Draw all possible molecular orbital combinations in benzene. Indicate which combinations are bonding and antibonding. Circle the degenerate orbitals. 4. (5 pt) Reacting bromine with a benzene ring produces the substitution product rather than the addition product. Which one of these products is more stable? Why is the substitution product favored over the addition product? Br Br Br Addition Product Substitution Product 5. (6pt) Circle the compounds that are aromatic according to the Hückle Rule. N N S N N 6. (8 pt) Explain why the following compounds are aromatic or not. Include Frost circles in your explanation. cyclobuta-1,3-diene anti-aromatic cyclohepta-2,4,6-trien-1-ylium aromatic 7. (5 pt) Would dibenzo-p-dioxin be aromatic, antiaromatic, or non-aromatic. Based on this, what would you expect the hybridization of the oxygens to be? O O 8. (8 pt) Give the reaction conditions for the following transformations: ? NO2 ? SO3H NO2 ? Br ? NH2 9. (8 pt) Identify the following as activating or deactivating groups. Indicate if they are meta or ortho-para directing groups. O Cl : OH 10. (8 pt) Give the products (some have more than 1) of the following reactions NO2 I2, 2 Cu2+ I2, 2 Cu2+ NH2 O I2, 2 Cu2+ I2, 2 Cu2+ O 11. (7 pt) Draw the reaction mechanism for the following reaction. Include the formation of the electrophile. Explain why the acyl electrophile is so stable. O Cl . AlCl3 O 12. (6 pt) Explain what is wrong with the following reactions: OH OH Cl AlCl3 NO2 HNO3, H2SO4 Cl Cl 13. (8 pt) Use retrosynthesis to propose a route to synthesize m-chlorobenzoic acid from benzene (3 steps are required). O Cl OH 14. (8 pt.) Circle the chiral centers on the following molecules N Cl S Br 15. (6 pt) Assign the following as R or S Cl H O P 16. (6 pt) Calculate the specific rotation for the following and indicate which direction (clockwise / counterclockwise) the light is being rotated: a. A 3.0 g sample of morphine dissolved in 10 mL of methanol in a 5 dm polarimeter which gives a observed rotation of -198º. b. A 1.0 g sample of sucrose dissolved in 8 mL of water in a 10 dm polarimeter which gives a observed rotation of 83.0º. 17. (8 pt) Identify the following pairs of molecules as constitutional isomers, enantiomers, diasteriomers, meso, or not isomers. H Br H3C H Br CH3 Cl Cl Cl H Br H3C H Br H3C NH NH HO Cl O HO O O 18. (8 pt) Label the pictured molecules as either the Re or the Si face. O O O Br Cl O O H 19. (4 pt) Hydrogen addition into the Si face of acetophenone (pictured) produces the R enantiomer, however propyl magnesium bromide addition forms the S enantiomer. Explain why. HO O H BrMg H2 (R)-1-phenylethanol acetophenone HO (S)-2-phenylpentan-2-ol 20. (6 pt) Label the indicated H’s as pro-R or pro-S. Ha Hb Ha Hb O Ha Hb Bonus (9 pt) Match the following structures with their uses and circle the chiral compounds: A) TNT, an explosive B) Coniine, a poisonous alkaloid found in hemlock C) Tryptophan, an essential amino acid required for serotonin production D) TCDD, a toxic dioxane contaminant in Agent Orange E) Oseltamivir, an antiviral sold under the name Tamiflu F) Peonindin, a plant pigment found in roses and cranberries N H Cl O Cl Cl O Cl HN H2N OH OCH3 NO2 O O O2N O NO2 OH O O HO HN O OH NH2 OH Bonus (3 pt) Azo dyes are brightly colored synthetic dyes. What about the structure of these organic compounds produces such vivid colors? O O O S N OH OH O S N N O OH N N OH HO O S N OH