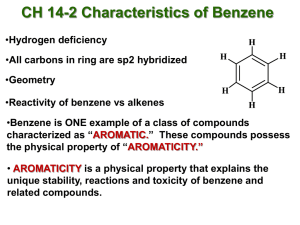
CHM 112
advertisement

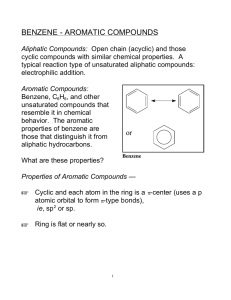
CHM 112 Spring 2002 WORKSHEET FOR AROMATIC COMPOUNDS 1. The common aromatic compounds contain the benzene ring which has three conjugated double bonds. It should act like an alkene and undergo addition but it does not. Explain why. Each carbon in the benzene ring has an unhybridized p orbital that is available to overlap with one on a neighboring carbon to form a second (double) bond. Instead, all of the p orbitals overlap and form a pi cloud of electrons above and below the plane of the carbon ring. The electrons are “delocalized”. This means that they are not in one set region to be used for an addition reaction at the site of two specific carbons. p orbitals on carbons 2. delocalized electrons form pi clouds Write the IUPAC names for each of the following compounds: CH Br CH I H C OH CH Cl NO 2-chlorophenol o-chlorophenol 1-hydroxy-2-chlorobenzene 3. 4-bromotoluene p-bromotoluene 1-bromo-4-methylbenzene 2-iodo-4-isopropyl nitrobenzene Write the structural formula for the following compounds. m-ethyltoluene 4-methyl-3-phenyl octane 1, 3, 5-tribromobenzene CH 3 H2 C HC H3C C H CH Br H2 C CH CH C H2 CH 3 C H2 Br Br