Kinetic Worksheet
advertisement

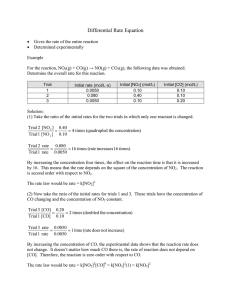
Kinetic Worksheet 1. How is the rate of a chemical reaction measured? 2. Write out a generic rate law for the reaction 2A + B2 --> 4C. 3. What does the order tell you? 4. How does temperature affect rates? 5. What is activation energy? 6. A (g) + 3B (g) 2C (g) Use the tabulated data to answer the questions about this reaction, which is carried out in a 1.0 L container at 25°C. Experiment 1 2 3 M [Ao] M [Bo] 0.10 0.20 0.10 0.10 0.20 0.20 Initial rate of formation of C, a. For experiment 1, give the initial rate of disappearance of i. A ii. B b. Determine the orders of A and B. c. Calculate the value of the rate constant and give its units. d. Write out the rate law for the reaction. 0.25 2.0 2.0 M min 7. The nitrogen dioxide (NO2) produced during driving is a health hazard. Chemists attempting to remove it have investigated the effect of heating it to high temperatures. At 300 °C the concentration of NO2 drops with time as in the table below. Find the order of reaction and the rate constant. 8. In automobile exhausts, the following reaction can occur between nitrogen dioxide and carbon monoxide. NO2(g) + CO(g) → NO(g) + CO2(g) To design better emission control systems, chemists need to know as much as possible about the kinetics of this reaction. The experimental rate law is r = k[NO2]2. Explain which of the two mechanisms below better represents this reaction. Mechanism A NO2 CO + O k1 (slow) Mechanism B NO + O k2 (fast) CO2 2NO2 k1 (slow) CO + NO3 k2 (fast) NO3+ NO NO2 + CO2 9. Cows digesting grass emit large quantities of global-warming methane gas into the atmosphere. As an atmospheric chemist, you are interested in knowing what role that methane plays in the cycling of chlorine in the atmosphere via the reaction: Cl(g) + CH4(g) → CH3Cl(g) + H(g) The rate constant at 25.0 °C is 6.02×107 M-1s-1. At 65,000 ft in the stratosphere, where the temperature is 60 °C, the rate constant is 1.08×107 M-1s-1.What is the activation energy for this reaction? 10. Given the following mechanism, write the overall reaction and the rate law for the overall reaction: A + B --> 2C C + A --> D SLOW FAST Challenge Question: The specific rate constant for the first-order decomposition of N2O5 (g) to NO2 (g) and O2 (g) is 7.48 x 10-3 s-1 at a given temperature. Find the length of time required for the total pressure in the system containing N2O5 at an initial pressure of 0.100 atm to rise to 0.155 atm.