Ch. 9 note packet
advertisement

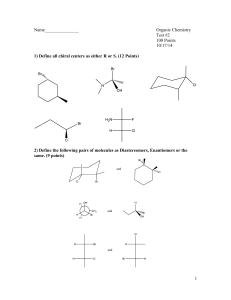
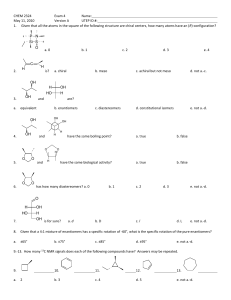
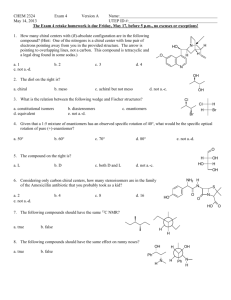
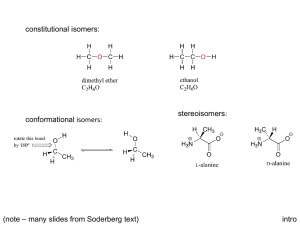
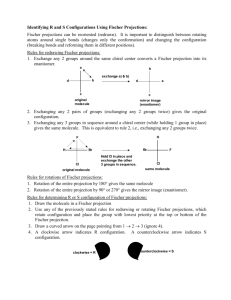
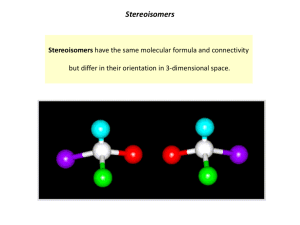
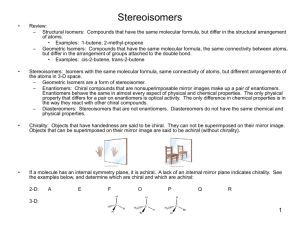
Chapter 9 - Stereoisomerism 9.1 Review of Isomerism Isomers 9.2 Enantiomers Enantiomer – 1) 2) Chiral ex’s: Achiral ex’s: Build It! 2-butanol, 2-methyl-2-butanol Wedge-bond Structual Drawing Fischer Projection Chiral Test: Does it have a tetrahedral stereocenter? mirror mirror • The solid, horizontal wedge bonds ( ) extend in front of the plane of the paper. • The dashed, vertical wedge bonds ( ) extend behind the plane of the paper. • Both solid and dashed wedge bonds are oriented with their wider ends nearer the viewer. Build It! 1-bromo-1-chloroethane, 1,1-dichloroethane, 1,2-dichloroethane Wedge-bond Structual Drawing Fischer Projection mirror mirror 1 9.3 Interpreting Structural Formulas of Enantiomers Build it: 1-bromo-1-chloroethane. The book is set up so that you can only rotate diagram 180°. Determining whether two structural drawings represent a pair of enantiomers or the same compound. Indicate whether each of the following pairs of structural drawings represents the same compound of a pair of enantiomers. (a) (b) 9.4 Nomenclature for Enantiomers • configuration determined by x-ray crystallography • Two systems R/S and D/L D/L System (Works if substituents include –H, -heteratom substituent (-OH or –NH2), -R1, -R2. Fischer Projections -R1 and -R2 extend backward (__________) -H and –heteroatom extend forward (__________) Fischer projection is oriented so -R1 (carbon w/ fewest H’s) is located upward and - R2 (most H’s) is located downward. 9.5 Properties of Enantiomers – OMIT Optical Activity & Specific Rotation Chemical Properties: Chiral Recognition Chiral reactivity depends on other reactants or the enzyme (biological catalyst) or both. • When reacting with achiral compounds, enantiomers usually have the same reactivity. • When reacting with chiral compounds or in reactions catalyzed by chiral enzymes, enantiomers usually have very large differences in reactivity. 2 Box 9.3 Synthetic Chiral Drugs • 40-50% drugs consist of compounds with one or more stereocenters. • Manufacturing produces a racemic mixture Body Responds: 1) Both enantiomers react but in different processes, one of which may produce an undesired effect on the organism. 2) One enantiomer reacts in a biological process and the other pases through the organism with no effect. Ex. Parkinson’s Disease Consequence – Drug – L-Dopa (L-3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine) Making non-racemic mixtures: 1) 2) 3