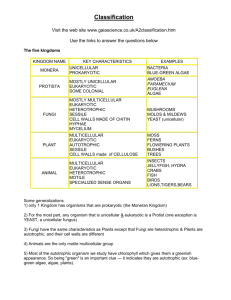
The Six Kingdoms (Organizing Biodiversity)
advertisement

Brainteaser Name three keys that unlock no doors. Answer Here Which of the following is NOT a characteristics of living things. A. Reproduction and Growth B. Metabolism C. Movement D. Cellular Organization Today you will 1. How living things are organized. 2. The difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. 3. The difference between autotrophs and heterotrophs. Let’s Review - Living Things grow and develop. reproduce. obtain and use materials and energy. respond to their environment. change over time. are based on a universal genetic code. are made up of units called cells. Maintain their internal environments. Let’s Review More What is Classification? •Grouping of objects or information based on similarities. •In Biology this is called Taxonomy. What is Taxonomy? The branch of biology concerned with the grouping and naming of organisms Who is Linnaeus? •Father of modern taxonomy •Developed the method of classification that is used today. •Classified organisms based on physical characteristics •Created the 7 taxonomic categories: What is Linnaeus’s System of Classification King Philip Came Over For Great Spaghetti Taxon – each level within a naming system. Kingdom (Most inclusive) Phylum Class Order Family Genus Species (Least inclusive or exclusive) King Phillip Came Over For Great Spaghetti 9 How are Living Things Organized? According to the 6 Kingdom system of classification. What are the 6 KINGDOMS? Animalia Plantae Fungi Protista Eubacteria Archaebacteria How are the Kingdoms Organized? Type of Cell prokaryotic/eukaryotic # of Cells - unicellular/multicellular Feeding - autotrophic/heterotrophic Cell Wall – present or not What is a Prokaryotic Cell What is a Eukaryotic Cell No Nucleus Nucleus What is Unicellular? Only one cell What is Multicellular? More than one cell What is an Autotroph? Make their own food What is a Heterotroph? Do NOT make their own food What is Kingdom Animalia? (that’s us!) What are the Characteristics of the Animalia Kingdom? Multicellular Heterotrophic Eukaryotic Do NOT have cell walls Terrestrial and aquatic What is the Plantae Kingdom? Plants ! The green stuff! What are the Characteristics of the Plantae Kingdom? Multicellular Autotrophic Eukaryotic Have cell walls with cellulose (that’s roughage to you & me) Terrestrial and aquatic, requiring sunlight What is the Kingdom Fungi? (the great recyclers) Rhizopus Ringworm What are the Characteristics of the Fungi Kingdom? MOST multicellular, a few unicellular (yeasts) Heterotrophic Eukaryotic Have cell walls with chitin Terrestrial, in warm, moist conditions What is Kingdom Protista? (a little of everything) Euglena Amoeba Vorticella What are the Characteristics of the Protista Kingdom? MOST unicellular, a few multicellular Some autotrophic & others heterotrophic Eukaryotic Some have cell walls with cellulose, some do not have cell walls at all Mostly aquatic What is Kingdom Eubacteria previously a part of the Kingdom Monera. Nostoc (photosynthetic) E. coli What are the Characteristics of the Eubacteria Kingdom? Unicellular Some autotrophic & others heterotrophic Prokaryotic Cell Wall – with peptidoglycans Found most everywhere (and most are not harmful!) What is Kingdom Archaebacteria The extremophiles! Thermophiles Yellowstone N.P. Hot Springs Halophiles in Great Salt Lake, Utah What are the Characteristics of the Archaebacteria Kingdom? Unicellular Some autotrophic & others heterotrophic Prokaryotic Cell Wall – without peptidoglycans. Unique RNA Found in extreme environments where other organisms cannot live How well did you do today? Which kingdom contains organism that are prokaryotic? a.Animalia b.Plantae c.Protista d.Eubacteria