Histology Part II: Connective Tissue
advertisement

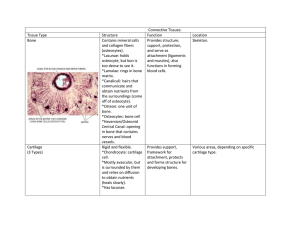
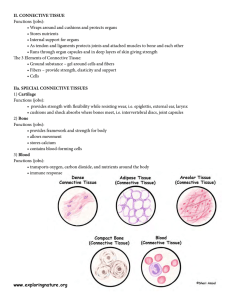
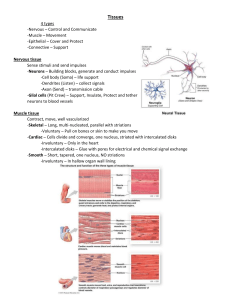
MMHS Anatomy Location and Description Location: Found throughout the body but never exposed to the external environment. Description: Made up of specialized cells. Contains extracellular protein fibers called “matrix”. “Ground Substance” fluid found throughout. May or May not be highly vascularized. Bone, Blood, Loose Connective, Adipose = Vascular Cartilage, Dense Connective = Poorly vascularized Functions of Connective Tissue 1. Provides a structural framework of the 2. 3. 4. 5. body. Transports Fluids Binds together other body tissues. Protection of vital internal organs. Stores long-term energy. Loose Connective Contains a disorganized “packing material” that fills spaces between organs and cushions and supports epithelia. Adipose tissue: looks like droplets of lipids: functions to pad and insulate the body. Nuclei are squished to the side. Dense Connective Collagen fibers dominated this tissue. Fibers are tightly packed and run parallel to each other. Fibers often have “wavy” appearance. Examples: tendons, ligaments, and elastic tissue. Blood Red blood cells (erythrocytes) = the most numerous and biconcave-shaped cells. Transport gases. White blood cells (leukocytes)= fewer in number; large, irregularly-shaped, fight diseases. Plasma = made up of a watery fluid. Platelets (thrombocytes)= fragments of cells that clot blood. Hyaline Cartilage Most common type of cartilage Collagen fibers are so closely packed and so appear to be absent.. Locations: Connections between ribs, coverings of elbow and knee. Compact Bone Made up of collagen fibers and calcium salts. Lacunae (compartments within bone) contain osteocytes. Bone tissue is highly vascularized = diffusion of gases occurs between osteocytes through canaliculi. Spongy “Cancellous” Bone Made up of bone columns called trabeculae. Lacunae contain osteocytes. Spongy Bone tissue contains red marrow. Found in the ends of long bones called epiphyses. Cushions impact during falls and distributes force to the compact bone. Contains many air spaces in the tissue.