Ionic Naming & Formula Writing Covalent Naming & Formula Writing
advertisement
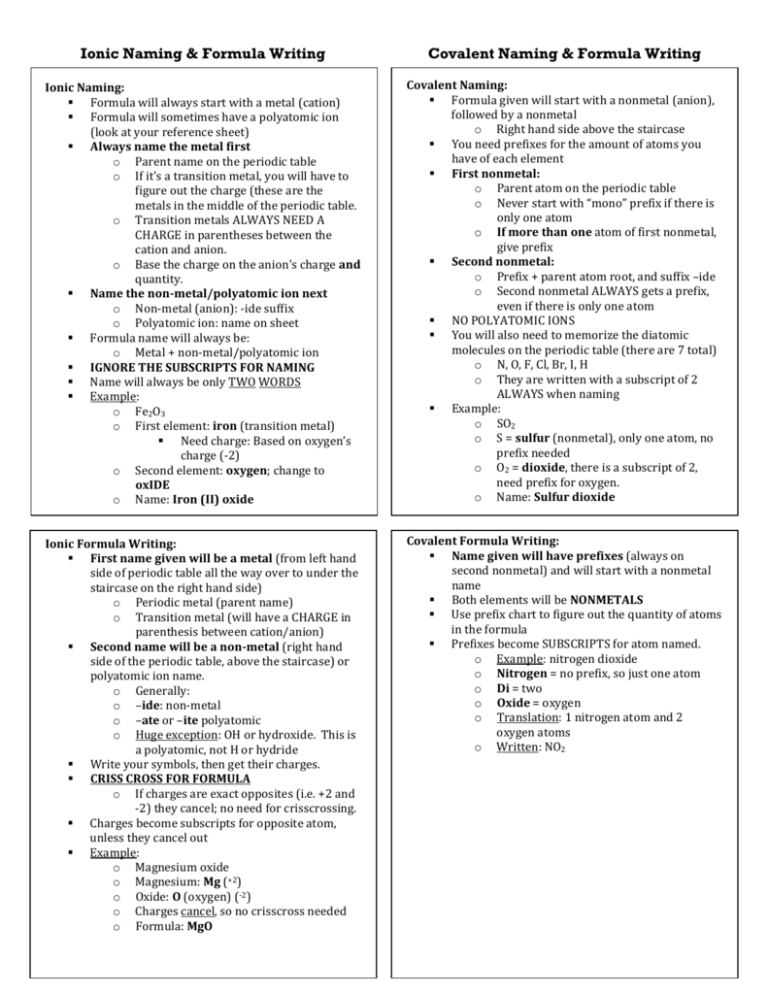
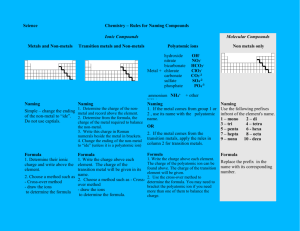
Ionic Naming & Formula Writing Covalent Naming & Formula Writing Ionic Naming: Formula will always start with a metal (cation) Formula will sometimes have a polyatomic ion (look at your reference sheet) Always name the metal first o Parent name on the periodic table o If it’s a transition metal, you will have to figure out the charge (these are the metals in the middle of the periodic table. o Transition metals ALWAYS NEED A CHARGE in parentheses between the cation and anion. o Base the charge on the anion’s charge and quantity. Name the non-metal/polyatomic ion next o Non-metal (anion): -ide suffix o Polyatomic ion: name on sheet Formula name will always be: o Metal + non-metal/polyatomic ion IGNORE THE SUBSCRIPTS FOR NAMING Name will always be only TWO WORDS Example: o Fe2O3 o First element: iron (transition metal) Need charge: Based on oxygen’s charge (-2) o Second element: oxygen; change to oxIDE o Name: Iron (II) oxide Covalent Naming: Formula given will start with a nonmetal (anion), followed by a nonmetal o Right hand side above the staircase You need prefixes for the amount of atoms you have of each element First nonmetal: o Parent atom on the periodic table o Never start with “mono” prefix if there is only one atom o If more than one atom of first nonmetal, give prefix Second nonmetal: o Prefix + parent atom root, and suffix –ide o Second nonmetal ALWAYS gets a prefix, even if there is only one atom NO POLYATOMIC IONS You will also need to memorize the diatomic molecules on the periodic table (there are 7 total) o N, O, F, Cl, Br, I, H o They are written with a subscript of 2 ALWAYS when naming Example: o SO2 o S = sulfur (nonmetal), only one atom, no prefix needed o O2 = dioxide, there is a subscript of 2, need prefix for oxygen. o Name: Sulfur dioxide Ionic Formula Writing: First name given will be a metal (from left hand side of periodic table all the way over to under the staircase on the right hand side) o Periodic metal (parent name) o Transition metal (will have a CHARGE in parenthesis between cation/anion) Second name will be a non-metal (right hand side of the periodic table, above the staircase) or polyatomic ion name. o Generally: o –ide: non-metal o –ate or –ite polyatomic o Huge exception: OH or hydroxide. This is a polyatomic, not H or hydride Write your symbols, then get their charges. CRISS CROSS FOR FORMULA o If charges are exact opposites (i.e. +2 and -2) they cancel; no need for crisscrossing. Charges become subscripts for opposite atom, unless they cancel out Example: o Magnesium oxide o Magnesium: Mg (+2) o Oxide: O (oxygen) (-2) o Charges cancel, so no crisscross needed o Formula: MgO Covalent Formula Writing: Name given will have prefixes (always on second nonmetal) and will start with a nonmetal name Both elements will be NONMETALS Use prefix chart to figure out the quantity of atoms in the formula Prefixes become SUBSCRIPTS for atom named. o Example: nitrogen dioxide o Nitrogen = no prefix, so just one atom o Di = two o Oxide = oxygen o Translation: 1 nitrogen atom and 2 oxygen atoms o Written: NO2