Photosynthesis, Respiration & Mitosis Notes
advertisement

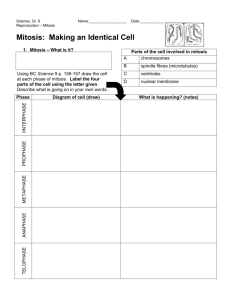
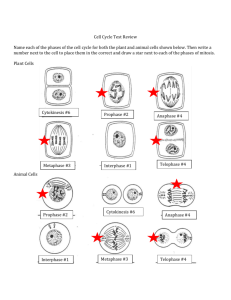
4.1 and 4.2 Notes A. Autotrophs vs. Heterotrophs •Autotrophs: make their own food (i.e. plants) Go through both photosynthesis AND cell respiration •Heterotrophs: do not make their own food (like animals) and get food from breaking down food molecules. ONLY RESPIRATION! B. ENERGY FLOWS! •ATP: an energy carrying molecule •Energy flows from the sun through all organisms •Energy is required for growth and reproduction, movement and transportation of materials across cell membranes. C. Photosynthesis formula D. Factors that affect photosynthesis •Includes temperature, light intensity, amount of water, oxygen and CO2 E. Cell Respiration formula 4.3 Notes A. Stages of Cell Division Stage 1: Interphase Stage 2: Mitosis A. Prophase B. Metaphase C. Anaphase D. Telophase Stage 3: Cytokinesis B. Stage 1: Interphase During interphase the cell grows, makes a copy of its DNA, and prepares to divide into two cells. ● During interphase the cell also copies all organelles needed for the new cell Chapter 4 Text of Notes (1) ● Replication is the process of making a copy of the DNA C. Stage 2: Mitosis During mitosis one copy of the DNA is distributed into each cell. Mitosis has four distinct phases 1. Prophase 2. Metaphase 3. Anaphase 4. Telophase D. Mitosis Phase 1: Prophase During Phase 1: Prophase chromatin in the nucleus condenses to form chromosomes. Pairs of centrioles move to opposite sides of the nucleus. E. Mitosis Phase 2: Metaphase During Phase 2: Metaphase the chromosomes line up across the center of the cell. At this time each chromosome attaches to a spindle fiber at its centromere. F. Mitosis Phase 3: Anaphase During Phase 3: Anaphase the centromeres split, each chromosome separates. At this point the cell stretches out as far as possible. G. Mitosis Phase 4: Telophase During Phase 4 Telophase the chromosomes become encased in their new nuclear envelope. H. Stage 3: Cytokinesis During Cytokinesis the cell membrane pinches in around the center of the cell, creating two distinct cells. Chapter 4 Text of Notes (2)