CH-10 Cell Division - Newark City Schools
advertisement

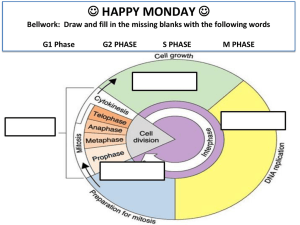
Mitosis Why do cells divide? • The larger a cell gets, the more demands it places on its DNA • As a cell gets larger, it has more trouble moving enough nutrients (food) and waste across its cell membrane Before a cell gets too large it divides. Cell division is the process by which a cell divides into two new daughter cells Cell division occurs in a series of stages or phases….. Interphase • Using Latin P&S, Interphase means – Between phase • Chromosomes are copied (number doubles) • At the beginning of this phase chromosomes appear threadlike and are known as chromatin, but by the end of this phase chromosomes have taken a new shape Interphase Prophase • MITOSIS BEGINS • Using Latin P&S, Prophase means – Before phase • Cell begins to divide • Centrioles appear and begin to move to opposite ends of the cell • Spindle fibers form between the centrioles • Nuclear membrane begins to break down Prophase Metaphase • Chromatids attach to spindle fibers • Chromatids are lined up in the MIDDLE Metaphase Anaphase • Chromatids separate and begin to move to opposite ends of the cell Anaphase Telophase • Using Latin P&S, Telophase means – End phase • Two new nuclei form • Chromosomes once again appear as chromatin (threads rather than rods) • MITOSIS ENDS Telophase Cytokinesis • Cell membrane moves inward to create two daughter cells – each with their own nucleus and identical chromosomes Cytokinesis