Nuclear Reactions Worksheet: Chemistry Practice

Nuclear reactions
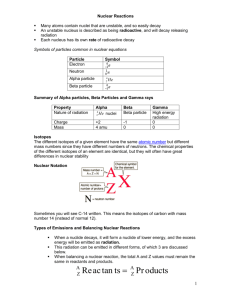
The stability of isotopes is based on the ratio of neutrons and protons in its nucleus. Although most nuclei are stable, some are unstable and spontaneously decay, emitting radiation. Each radioactive isotope has a specific mode and rate of decay (half-life).
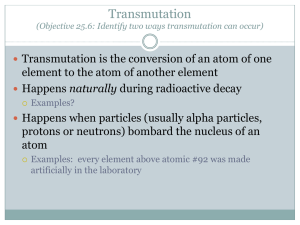
A change in the nucleus of an atom that converts it from one element to another is called transmutation . This can occur naturally or can be induced by the bombardment of the nucleus by high-energy particles.
Spontaneous decay can involve the release of alpha particles, beta particles, or gamma radiation from the nucleus of an unstable isotope.
These emissions differ in mass, charge, and ionizing power, and penetrating power. Nuclear reactions include natural and artificial transmutation, fission, and fusion. There are benefits and risks associated with fission and fusion reactions. Nuclear reactions can be represented by equations that include symbols which represent atomic nuclei (with the mass number and atomic number), subatomic particles
(with mass number and charge), and/or emissions such as gamma radiation.
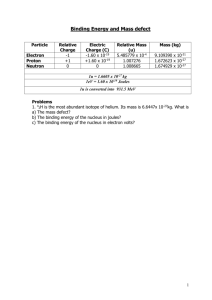
Energy released in a nuclear reaction (fission or fusion) comes from the fractional amount of mass converted into energy.
Nuclear changes convert matter into energy.
Energy released during nuclear reactions is much greater than the energy released during chemical reactions.
1.
Which type of radiation has zero mass and zero charge?
(1) alpha (2) beta (3) neutron (4) gamma
2.
Which kind of nuclear radiation has high energy and no mass?
1. alpha 2. beta 3. gamma 4. neutron
3.
Given the equation: N-14 + He-4
→
X + O-17 when the equation is balanced correctly, which particle is represented by X?
(1) alpha particle (2) neutron (3) proton (4) positron
4.
Which process converts an atom from one element to another, when the nucleus of an atom is bombarded with high-energy particles?
(1) artificial transmutation (2) natural transmutation
(3) addition polymerization (4) condensation polymerization
5.
Which equation represents an artificial transmutation?
6.
In the reaction shown the X represents
1. an alpha particle 2. a beta particle 3. an electron 4. a proton
7.
Given the equation shown. Which particle is represented by the letter X?
1. an alpha particle 2. a beta particle 3. a neutron 4. a proton
8.
Given the nuclear reaction. What is represented by X?
1. an alpha particle 2. a beta particle 3. a proton 4. a positron
9.
Which equation represents a fusion reaction?
10.
A fission reaction is similar to a fusion reaction in that both reactions involve
(1) collisions between nuclei of high atomic number
(2) collisions between nuclei of low atomic number
(3) the conversion of mass to energy
(4) the conversion of energy to mass
11.
Which statement best describes what happens in a fission reaction?
(1) Heavy nuclei split into lighter nuclei.
(2) Light nuclei form into heavier nuclei.
(3) Energy is released and less stable elements are formed.
(4) Energy is absorbed and more stable elements are formed.
12.
The diagram represents a nuclear reaction in which a neutron bombards a heavy nucleus. Which type of reaction does the diagram illustrate?
1. fission 2. fusion 3. alpha decay 4. beta decay