Alpha particle
advertisement

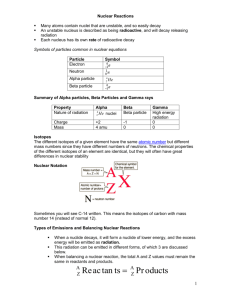
STAAR Chemistry Review Topic: Nuclear Chemistry TEKS 12 – The student understands the basic processes of nuclear chemistry. Student Expectation (SE) • Student Expectation (SE) 12A – describe the characteristics of alpha, beta, and gamma radiation. INDEX CARD TIME! TITLE: nuclear particles FRONT: characteristics of nuclear particles BACK: Draw a table to summarize the symbol, the charge, mass (relative); speed (relative) and penetration power (relative) of alpha, beta and gamma ray. Nuclear particles • Alpha particle () – helium nucleus Beta particle (-) electron Gamma () high-energy photon 4 2 0 -1 He e charge 2+ 1- 0 Stopped by: paper Metal Foil lead A. Types of Radiation • Alpha particle () – helium nucleus 4 2 He Alpha Emission – an alpha particle () is 2 protons and 2 neutrons (or a helium atom) bound together and is emitted from the nucleus during some kinds of radioactive decay. 210 206 Po Pb + 84 82 Paper or clothes will shield you from alpha particles. 4 He 2 B. Types of Radiation Beta particle (-) electron 0 -1 e Beta Emission – a beta particle () is an electron emitted from the nucleus when a neutron is converted to a proton 14 C 6 14 N 7 + 0 -1 Metal foil will shield you from beta particles. C. Types of Radiation Gamma Emission – gamma rays () are highenergy electromagnetic waves emitted from a nucleus. Very similar to light, but is much more dangerous. Lead or concrete will protect you from gamma rays. Gamma () high-energy photon Student Expectation (SE) • Student Expectation (SE) 12B - describe radioactive decay process in terms of balanced nuclear equations; INDEX CARD TIME! TITLE: Radioactive Decay FRONT: What are radioactive decay processes BACK: Write the definition of radioactive decay processes and give examples of balanced nuclear reactions. Balancing Nuclear Equations • In nuclear equations the total of the atomic number and the total of the mass number must be equal on both sides of the equation. Example: 9 4 12 1 Be + He C + n 4 2 6 0 Mass Number: 9+4 = 13 12+1 = 13 Atomic Number: 4+2 = 6 6+0 = 6 Student Expectation (SE) • Student Expectation (SE) 12C – compare fission and fusion reactions. INDEX CARD TIME! TITLE: Fission and Fusion FRONT: Difference between Fission and Fusion reactions BACK: Write down the definition of Fission and Fusion reactions emphasizing the difference between them. Nuclear Fission reaction – the splitting of a nucleus into smaller fragments (the splitting is caused by bombarding the nucleus with neutrons). This process releases enormous amounts of energy. A nuclear chain reaction is a reaction in which the material that starts the reaction (neutron) is also one of the products and can be used to start another reaction. Nuclear Fusion Reaction * combining of two nuclei to form one nucleus of larger mass, usually very small atoms of hydrogen and helium are used. 2 1 H H 3 1