Nuclear Group Quiz! Name Score________ Answer each of the
advertisement

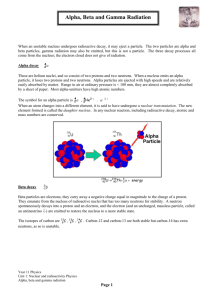
Nuclear Group Quiz! Name _________________________________________________ Score________ Answer each of the following questions regarding radioactivity. (a) Write the nuclear equation for decay of 234 94 Pu by alpha emission. (b) Account for the fact that the total mass of the products of the reaction in part (a) is slightly less than that of the original 234 94 Pu . (c) Describe how , , and rays each behave when they pass through an electric field. Use the diagram below to illustrate your answer. (d) Why is it not possible to eliminate the hazard of nuclear waste by the process of incineration? Answer: 4 (a) 234 94 Pu 2 + 230 92 U Due to a printing error, the student’s answer booklet had the Pu-239 isotope. Therefore, the following is a valid response. 239 94 Pu 24 + 235 92 U (b) This mass defect has been converted into energy. E = mc2 (c) An alpha particle, or He nuclei, has a 2+ charge and would be attracted to the (-) side of the electric field. A beta particle, , or electron, has a single negative charge and is attracted to the positive side of the electric field, but since it is much lighter and faster than an alpha it would not be as strongly deflected. Gamma, , rays are not charged and, therefore, not deflected by the electric field. (d) The half-life of a radionuclide is independent of its environment. Incineration will neither accelerate its decay nor render it non-radioactive. 8) 1997 (a) 94-Pu-239 ---> 2-He-4 + 92-U-225 Notes; One point is earned for [He] (or ), one point for correct total mass number in products, and one point for consistent atomic numbers and symbols. Full credit is also earned for correct decay starting with Pu-234 (as was printed on the green insert) (b) Missing mass is converted to energy (or "E=mc2") Notes; No point earned for just mentioning "mass defect". (c) In words, or drawn on diagram: path of particle bends toward negative (-) plate, 1 point path of particle bends toward positive (+) plate, 1 point path of ray is undeflected. 1 point (d) Incineration (combustion, oxidation) is a chemical process AND as such it has no effect on a nuclear process (decay). 1 point Notes; No point for thermodynamic, kinetic, or equilibrium arguments. No point earned for "dispersion of material is bad for the environment" or similar statements. C 1. When 214 84𝑃𝑜 decays, the emission consists consecutively of an alpha particle, then two beta particles, and finally another alpha particle. The resulting stable nucleus is (A) 206 83𝐵𝑖 (B) 210 83𝐵𝑖 206 (C) 82𝑃𝑏 (D) 208 82𝑃𝑏 210 (E) 81𝑇𝑙 A 2. The radioactive decay of (A) beta particle emission (B) alpha particle emission (C) positron emission (D) electron capture (E) neutron capture 14 6𝐶 to 14 7𝑁 occurs by the process of 131 D 3. 251 98𝐶𝑓 2 n + 54𝑋𝑒 + __ What is the missing product in the nuclear reaction represented above? (A) 118 42𝑀𝑜 118 (B) 44𝑅𝑢 (C) 120 42𝑀𝑜 (D) 120 44𝑅𝑢 122 (E) 46𝑃𝑑 4) Which of these nuclides is most likely to be radioactive? 27 A) 60 B) 13 Al C) 189 D) 1428 Si E) 28 Ni 88 Ra Answer: C 178 82 Pb 13 25) In the nuclear transmutation, 16 8 O (p, α) 7 N, what is the bombarding particle? A) an alpha particle B) a beta particle C) a gamma photon D) a proton E) a phosphorus nucleus Answer: D 6) The mass of a proton is 1.00728 amu and that of a neutron is 1.00867 amu. What is the binding energy (in J) of a 60 27 Co nucleus? (The mass of a cobalt-60 nucleus is 59.9338 amu.) A) 2.74 × 10-19 B) 9.12 × 10-28 C) 4.94 × 10-13 D) 8.20 × 10-11 E) 2.74 × 10-16 Answer: D