File - sgribble

Study Guide Honors Chemistry I
Identify the four fundamental forces in the universe and their role in the atom.
Mid-Quarter 2
Discuss the role of the neutron to proton ration.
Utilize the zone or belt of stability (proton to neutron ratio) to make predictions of nuclide stability.
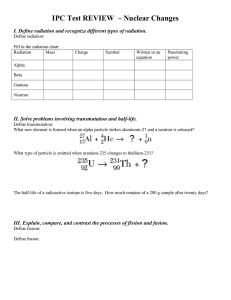
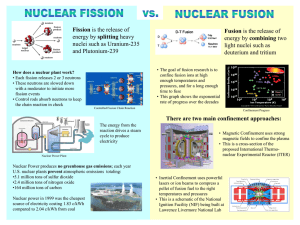
Identify the types of nuclear reactions – alpha, beta, gamma, positron, electron capture, fission, fusion.
Write and balance nuclear equations.
Identify the source of elements smaller than iron and elements heavier than iron.
Solve problems of half-life. This requires the use of exponents, fractions, decimal, percentages and logs.
Compare and contrast r and s processes (“Where do Chemical Elements Come From”
Contrast the nuclear activity in small, medium and large stars.
Discuss the role of fusion, beta decay and in the creation of elements.
Discuss the two forces that are at work in living stars.
Sequence the events in a large star’s life from being mostly hydrogen to being a supernova.
Recognize that the stability of the nucleus is related to the number of neutrons relative to protons and that the nucleus contains shells of neutrons.
Give examples of isotopes.
Explain why a star collapses.
Recognize applications of nuclear science.
Be able to use decimal and scientific notation interchangeably.
Place numbers in scientific notation on a number line.
Carry out conversions: metric/metric, metric/English and other proportional story problems using dimensional analysis.
Alpha
Beta
Gamma
Positron
Electron capture
Fission
Fusion
Nuclide
Radioactive
Radioactivity
Half-life s process r process
Zone (belt) of stability
Neutron to proton ratio
Dimensional analysis