12. Middle Ages (Must Know)
advertisement

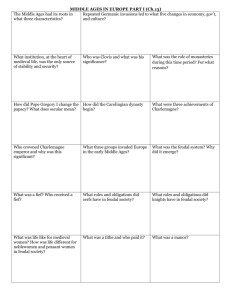
1. After the Fall of Rome (400-600 CE) A. Europe was in upheaval and chaos; the Germanic tribes controlled all of Western Europe. B. There was no longer a strong, central government. C. There was a decline in learning and a loss of the Greco-Roman heritage. D. The only strong institution that remains powerful and influential was the CATHOLIC CHURCH. 2. The Rise of Feudalism A. This DECENTRALIZED political system developed as a response to the collapse of a strong central government and Viking invasions (need for protection). B. Feudalism provided order and stability in a time of weakened central governments. C. The most powerful people in the feudal system were LANDOWNERS; LAND = POWER. D. Feudalism resulted in a very RIGID SOCIAL STRUCTURE. 1. Peasants were seldom able to change their social status. 2. There were SHARP SOCIAL DISTINCTIONS (classes) that divided European society. 3. An individual’s social status in feudal Europe was determined by birth. 4. There was LIMITED SOCIAL MOBILITY. E. The economic system that developed in feudal Europe was MANORIALISM. 1. Stressed the importance of LAND OWNERSHIP. 2. Peasants worked the land on an estate, called a MANOR and paid a tax to their lord 3. The AGE OF CHIVALRY- Chivalry was the CODE OF CONDUCT for KNIGHTS based on a complex set of ideals that demanded a knight fight bravely in defense of three masters: his earthly feudal lord, his heavenly lord, and his chosen lady. The ideal knight was loyal, brave, and courteous. 3.The Power of the Roman Catholic Church a. After the fall of Rome, the Catholic Church became the new CENTRAL AUTHORITY during the Middle Ages. b. The Church provided stability, order and unity in a time of chaos and disorder. c. The Church was the MOST POWERFUL FORCE in Medieval Europe and had a lot of political influence. d. The church had a very strong influence on daily life; religion was a way of life that governed western Europeans in the Middle Ages from birth to death. 4. Medieval Art and Architecture a. The style of art and architecture during the middle ages was called GOTHIC. The characteristics of GOTHIC ART are:stained glass windows ,tall spires, flying buttresses, pointed arches, ribbed vaults b. The architectural accomplishments of medieval Europe reflected RELIGIOUS themes and beliefs. c. All art, music and philosophy of the middle ages dealt with RELIGIOUS THEMES. 5. The Crusades (1096 – 1291) a. The Crusades were a series of wars of conquests and invasions in the Middle East led by western European Christians. b. The motives for fighting the Crusades were: 1. The Christian church wanted to recapture the “holy land” (Jerusalem) from the Islamic rulers. 2. Desire for wealth from the Middle East. 3. Desire of knights to be released from feudal obligations. 4. Knights fought in order to be forgiven of sins. c. The Crusades were largely UNSUCCESSFUL in their original intentions but still brought about many desirable changes in Western Europe. d. Crusades are often referred to as “History’s most successful failures.” e. There were many INDIRECT RESULTS OF THE CRUSADES: 1. There was a growth in trade between Europe and the Middle East and Asia 2. Contact with the Muslim and Byzantine worlds brought new ideas toWestern Europe. 3. Europeans had a new demand for Middle Eastern and Asian goods. 4. The culture and technology of Asia and the Middle East spread to Western Europe (major cultural diffusion). 5. There was a RENEWAL OF LEARNING in Western Europe as a result of the Crusades. 6. Overall, there was an INCREASE IN TRADE AND COMMERCE. f. Other results from the crusades were: 1. Development of the European middle class (merchants and traders) which eventually weakened the feudal system. 2. Increased tensions between the Muslims and the Christians. BIG IDEAS: