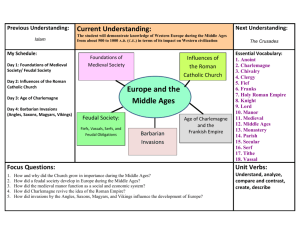
Chapter 13 Section 1: Charlemagne Unites Germanic Kingdoms
advertisement
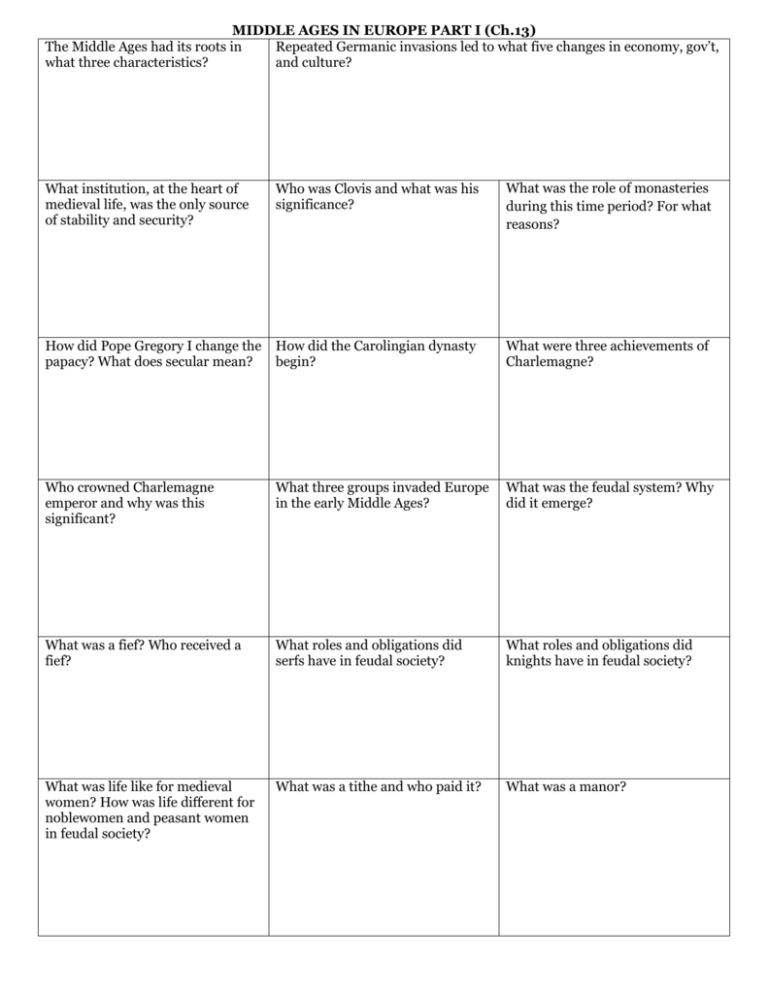
MIDDLE AGES IN EUROPE PART I (Ch.13) The Middle Ages had its roots in Repeated Germanic invasions led to what five changes in economy, gov’t, what three characteristics? and culture? What institution, at the heart of medieval life, was the only source of stability and security? Who was Clovis and what was his significance? What was the role of monasteries during this time period? For what reasons? How did Pope Gregory I change the papacy? What does secular mean? How did the Carolingian dynasty begin? What were three achievements of Charlemagne? Who crowned Charlemagne emperor and why was this significant? What three groups invaded Europe in the early Middle Ages? What was the feudal system? Why did it emerge? What was a fief? Who received a fief? What roles and obligations did serfs have in feudal society? What roles and obligations did knights have in feudal society? What was life like for medieval women? How was life different for noblewomen and peasant women in feudal society? What was a tithe and who paid it? What was a manor? What was medieval warfare like? What technologies and weapons were used? What responsibilities did a knight have according to the code of chivalry? How did medieval literature portray warfare, castle life, and chivalry? How did the sword analogy of Gelasius I apply to religious and political conflict in the Middle Ages? How was the Catholic Church organized/structured? How was religion a unifying force? What are sacraments? Define excommunication. Why were excommunication and interdict used? How did the practice of lay investiture create conflict between the pope and emperor? How was this resolved? Why were German states not able to unify in the Middle Ages? What were three or four of the problems troubling the Catholic Church? MIDDLE AGES REVIEW PART II (Ch.14) How was the church What was the Papal Curia? reorganized/restructured? Who were friars and how were they different from monks? What were three orders of friars? Describe Gothic architecture. Describe Romanesque architecture and why cathedrals changed to Gothic style. Name one famous Gothic cathedral in Europe. What was the primary reason for the Crusades? Who made the official call for the Crusades? What was the Reconquista? What was the Inquisition? What were some of the effects of the Crusades? How and why did the food supply in Europe increase in the later Middle Ages? (Ch.14.2) What was a guild and what was its purpose? What was the Commercial Revolution? How did business and banking develop? Describe urban life in the growing towns & cities of medieval Europe. How did contact w/Muslims in the Crusades contribute to the expansion of trade and learning for Europe? Who were Thomas Aquinas and the Scholastics (no, they were not a band)? What was the conflict between William the Conqueror and Harold Godwinson regarding? What was William the Conqueror’s invasion of England known as? What was the outcome of this invasion? What is the significance of common law developed in England. Why did nobles force King John to sign the Magna Carta? What was stated in the Magna Carta? Why is it significant? What was parliament? What was the Estates-General? What democratic traditions were emerging in England and France? What was the Great Schism and what impact did it have for the Church? Why did John Wycliffe challenge the Church? How did the bubonic plague (Black Death) originate and how did it spread? What were the effects of the Black Death? Why did the Hundred Year’s’ War begin and who was it between? What was the outcome of the Hundred Years’ War. What were the effects of the Hundred Years’ War?