Review Sheet- Key - Newark Central Schools
advertisement
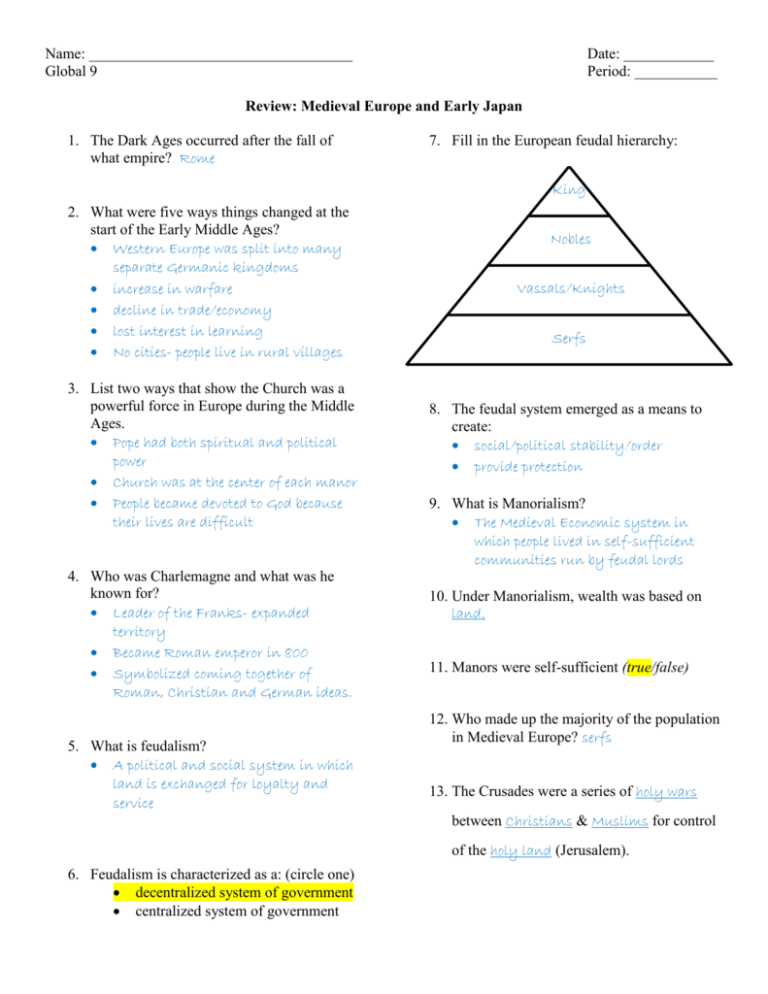
Name: ___________________________________ Global 9 Date: ____________ Period: ___________ Review: Medieval Europe and Early Japan 1. The Dark Ages occurred after the fall of what empire? Rome 7. Fill in the European feudal hierarchy: King 2. What were five ways things changed at the start of the Early Middle Ages? Western Europe was split into many separate Germanic kingdoms increase in warfare decline in trade/economy lost interest in learning No cities- people live in rural villages 3. List two ways that show the Church was a powerful force in Europe during the Middle Ages. Pope had both spiritual and political power Church was at the center of each manor People became devoted to God because their lives are difficult 4. Who was Charlemagne and what was he known for? Leader of the Franks- expanded territory Became Roman emperor in 800 Symbolized coming together of Roman, Christian and German ideas. 5. What is feudalism? A political and social system in which land is exchanged for loyalty and service Nobles Vassals/Knights Serfs 8. The feudal system emerged as a means to create: social/political stability/order provide protection 9. What is Manorialism? The Medieval Economic system in which people lived in self-sufficient communities run by feudal lords 10. Under Manorialism, wealth was based on land. 11. Manors were self-sufficient (true/false) 12. Who made up the majority of the population in Medieval Europe? serfs 13. The Crusades were a series of holy wars between Christians & Muslims for control of the holy land (Jerusalem). 6. Feudalism is characterized as a: (circle one) decentralized system of government centralized system of government 14. What were the results of the crusades? (If Turks Traveled, They would Trade) 21. Draw Japan’s feudal hierarchy. Em pero r Improvements (ships, maps, explorers) Feudalism declines Turks control the Holy Land Travel increases around the world Trade increases between Europe and the Middle East which leads to more cultural diffusion 15. What was the black death? The bubonic plague that killed 1/3 of the population. It started in China and spread through the Middle East to Europe. 16. Where did it start and spread to? It started in China and spread to the Middle East and Europe 17. What caused it to spread? Fleas (traveling on rats) spread the disease. An increase in trade led to an increase in the spread of the disease. 18. What is a chain of islands called? Archipelago Shogun Daimyo Samurai Peasants/Merchants 22. Who held the most real power in Japanese feudalism? Shogun 23. How are European chivalry and Japanese Bushido similar? Both are codes of conduct the warriors in the society must follow 24. Tokugawa is the name of the warrior family that ruled Japan from 1303-1863. 25. The Tokugawa Shogunate led to an increase in: social order/ stability 19. Most of Japan is covered in which geographic feature? How did they adapt? Mountains- They used terrace farming peaceful conditions trade and travel 20. Japan’s population and culture growth of cities High population density (true/false) Have a true respect for nature (true/false) Homogeneous society: people have the same genes, ethnicity and culture Ethnocentric: belief that your culture is superior Shintoism: belief that spirits exist in nature Selective borrowing: taking on only certain aspects of a culture (Japan mostly borrowed from China and Korea) 26. The Tokugawa shoguns enforced a policy of isolationism. By 1639 they had banned almost all contact with the outside world.











