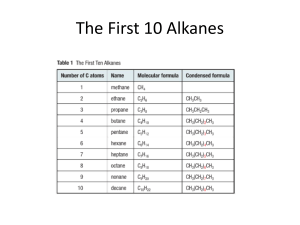
Name: Chem 22 Final exam Spring `00 What product is formed when
advertisement

Name: Chem 22 Final exam Spring ‘00 1. What product is formed when 2,2-dimethylcyclohexanol undergoes acidcatalyzed dehydration? a) b) c) d) e) 1,1-dimethylcyclohexene 2,2-dimethylcyclohexene 1,3-dimethylcyclohexene 1,2-dimethylcyclohexene 3,3-dimethylcyclhexen 2. What compound is formed from the acid-catalyzed rea tion of 2,3-epoxybutane with methanol? a) b) c) d) e) ethylene glycol 2-methoxy-3-butanol 2,3-butandiol 3-ethoxy-2-butanol 3-methoxy-2-butanol 3. Which of the following statements is true? a) Thiols have a pka values of about 16, and they are stronger acids than alcohols. b) Thiols have a pka values of about 16, and they are weaker acids than alcohols c) Thiols have a pka values of about 10, and they are stronger acids than alcohols d) Thiols do not have a pka values. e) Thiols have a pka values of about 10, and they are weaker acids than alcohols 4. Which of the following is not a true statement? a) In an organometallic compound, the carbon bonded to the metal is the nucleophile. b) An epoxide is more reactive than an ether. c) In a Hofmann elimination, a proton is removed from the beta carbon that is bonded to the greater number of hydrogens. d) Thioethers are also called sufides 5. What do PBr3, PCl3, and SOCl2 have in common? a) they convert alcohols into alkyl halides b) a and c c) they convert an alcohol into an intermediate that has a leaving group that can be displaced by a halide ion. d) They react with alcohols without forming an intermediate e) They undergo an E2 reaction with an alcohol. 6. What kind of reactions do aromatic compounds such as benzene undergo? a) b) c) d) e) electrophilic aromatic substitution reactions nucleophilic addition reactions electrophilic aliphatic substitution reactions electrophilic addition reactions nucleophilic aromatic substitution reactions. 7. What is the major product formed from the reaction of benzene with isobutyl chloride and AlCl3? a) b) c) d) e) 2-methyl-1-phenylpropane 2-phenylbutane isobutylbenzene 2-methyl-2-phenylpropane 1-phenylbutane 8. Which of the following is the most activating substituent for electrophilic aromatic substitution? a) b) c) d) e) –N(CH3)3+ - NH2 –NO2 –CH2NHCH3 –NH-C-(=O)-CH3 9. Which sequence of reactions will convert benzene into 2-phenylethanol? a) b) c) d) e) (1) Br2/FeBr3 (2) Mg/Et2O (3)ethylene oxide (4) H+ (1) ethylene oxide (2) H+ (3) Br2/FeBr3 (4) Mg/Et2O (1) Mg/Et2O (2) Br2/FeBr3 (3) propylene oxide (4) H+ (1) Br2 (2)Mg/Et2O (3) propylene oxide (4) H+ (1) Br2/FeBr3 (2) Mg/Et2O (3) propylene oxide (4) H+ 10. Which of the following compounds is the most acidic? (the substituents are parasubstuents.) a) b) c) d) e) O2NCH2-C6H4-COOH CH3-C6H4-COOH O=CH-C6H4-COOH O2N-C6H4-COOH CH3-C6H4-COOH 11. Which of the following represents the correct order of relative reactivity in a nucleophilic acy substitution reaction? a) b) c) d) e) acyl halides> esters> acid anhydrides> amides acyl halides> acid anhydrides> esters> amides acid anhydrides> acyl halides> esters> amides amides> carboxylic acids> acid anydrides> acyl halides esters> acid anhydrides> acyl halides> amides 12. Which of the follwing is not a true statement? a) An acid anhydride reacts with an alcohol to form an ester and a carboxylic acid. b) An acyl halide reacts with water to form a carboxylic acid. c) An acyl halide reacts with an amine to form an amide d) An ester reacts with an amine to form an amide. e) An amide reacts with an alcohol to fomr an ester. 13. Which of the followng reagents can be used to convert a carboxylic acid into an acyl chloride? a) b) c) d) e) PCl3 a and c SOCl2 SO2Cl SOCl 14. Which of the following is the best leaving group? a) b) c) d) e) CH3COOHOClNH3 NH2- 15. What product is formed when formic acid reacts with methyl amine at room temperature? a) No reaction occurs b) CH3COO-NH4+ c) HC (=O)-NH2 d) HCOO-CH3NH3+ e) HC(=O)-N(CH3)2 16. Which of the following compounds is the least reactive towards nucleophilic attack? a) b) c) d) e) acetone diisopropyl ketone methyl propyl ketone formaldehyde acetaldehyde 17. Carbonyl compounds can be reduced to alcohols using sodium borohydride followed by addition of H+/H2O. Which statement best describes the mechanism? a) addition of a hydrogen radical, flowed by addtion of a second hydrogen radical b) addition of a proton, followed by addition of a hydride ion c) addition of a hydride ion, followed by addition of water d) addition of a hydride ion, folloed by addition of a proton e) addtion of a hydride ion and a proton more or less at the same time 18. Which of the following describes “reductive amination?” a) an aldehyde or a ketone + a tertiary amine + H2/zeolite b) an aldehyde or a ketone + ammonia or a primary or a secondary amine + H2/Raney Ni c) an aldehyde or a ketone + ammonia or a primary or a secondary amine + H2O/Raney Ni d) an aldehyde or a ketone + ammonia or a primary or a secondary amine + H2/zeolite e) an aldehyde or a ketone + ammonia or a primary or a secondary amine + H2/zeolite 19. Which of the following reaction will form an alkane a) b) c) d) an aldehyde + a Griganard reagent a ketone + NH2NH2/HO-/heat an aldehyde + H+/H2O an aldehyde + sodium borohydride followed by H+/H2O 20. What sequence of reactions will conver CH3-C(=O)-CH2CH=O to CH3CH(OH)CH2CH=O? a) b) c) d) e) (1) H2/Pt (2) PCC (1) KMnO4/HO- (2) H+/H2O (1) HOCH2CH2OH/H+ (2) NaBH4 (3) H+/H2O (1) NaBH4 (2) H+/ H2O (1) LiAlH4 (2) H+/H2O 21. Which of the follwing reactions is neither an oxidation nor a reduction? a) Reaction of an alkene with Ozone b) Reaction af an alkene with a perocyacid c) Reaction of an alkene with hydrogen gas in the presence of a metal catalyst. d) Reaction of an alkene with water e) Reaction of an alkene with bromine 22. What product is obtained when cyclohexene reacts with a cold, basic solution of potassium permangante? a) b) c) d) 23. a cis diol with both OH groups in axial positions a cis diol with both OH groups in equatorial positions a trans diol with both OH groups in equatorial positions a cis dil with one OH group in an axial position and the other in an equatorial position.