Chem 3.5 Answers #6
advertisement
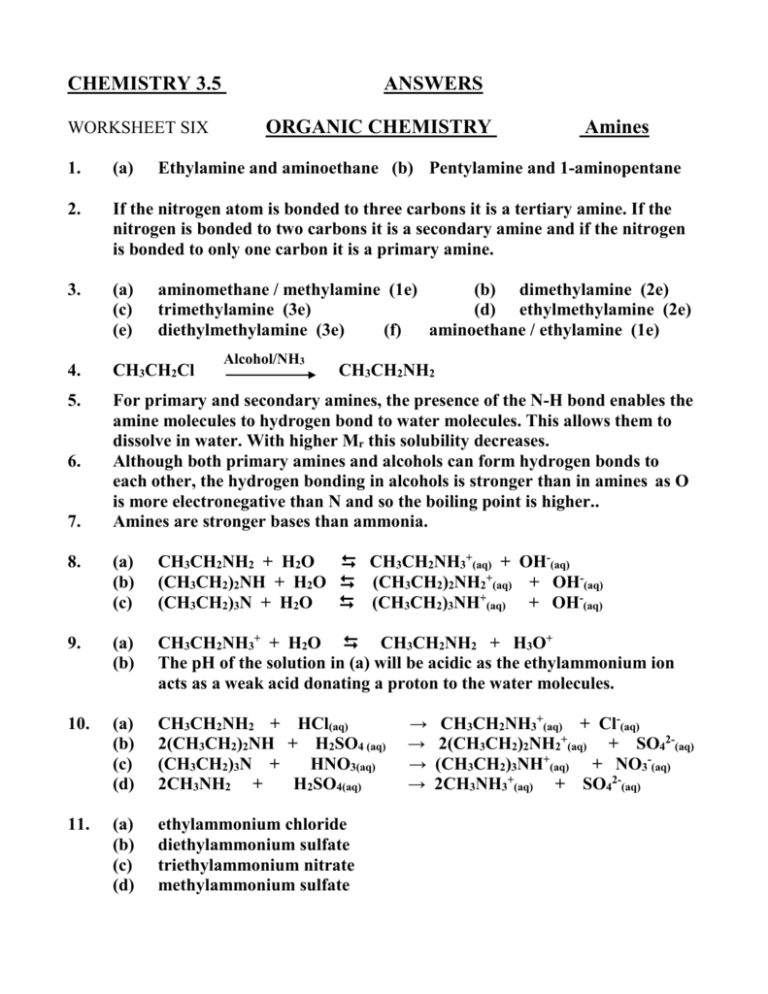
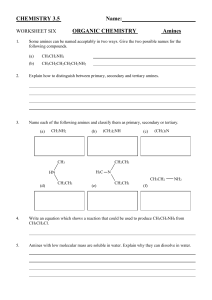
CHEMISTRY 3.5 WORKSHEET SIX ANSWERS ORGANIC CHEMISTRY Amines 1. (a) 2. If the nitrogen atom is bonded to three carbons it is a tertiary amine. If the nitrogen is bonded to two carbons it is a secondary amine and if the nitrogen is bonded to only one carbon it is a primary amine. 3. (a) (c) (e) 4. CH3CH2Cl 5. For primary and secondary amines, the presence of the N-H bond enables the amine molecules to hydrogen bond to water molecules. This allows them to dissolve in water. With higher Mr this solubility decreases. Although both primary amines and alcohols can form hydrogen bonds to each other, the hydrogen bonding in alcohols is stronger than in amines as O is more electronegative than N and so the boiling point is higher.. Amines are stronger bases than ammonia. 6. 7. Ethylamine and aminoethane (b) Pentylamine and 1-aminopentane aminomethane / methylamine (1e) (b) dimethylamine (2e) trimethylamine (3e) (d) ethylmethylamine (2e) diethylmethylamine (3e) (f) aminoethane / ethylamine (1e) Alcohol/NH3 CH3CH2NH2 8. (a) (b) (c) CH3CH2NH2 + H2O CH3CH2NH3+(aq) + OH-(aq) (CH3CH2)2NH + H2O (CH3CH2)2NH2+(aq) + OH-(aq) (CH3CH2)3N + H2O (CH3CH2)3NH+(aq) + OH-(aq) 9. (a) (b) CH3CH2NH3+ + H2O CH3CH2NH2 + H3O+ The pH of the solution in (a) will be acidic as the ethylammonium ion acts as a weak acid donating a proton to the water molecules. 10. (a) (b) (c) (d) CH3CH2NH2 + HCl(aq) 2(CH3CH2)2NH + H2SO4 (aq) (CH3CH2)3N + HNO3(aq) 2CH3NH2 + H2SO4(aq) 11. (a) (b) (c) (d) ethylammonium chloride diethylammonium sulfate triethylammonium nitrate methylammonium sulfate → → → → CH3CH2NH3+(aq) + Cl-(aq) 2(CH3CH2)2NH2+(aq) + SO42-(aq) (CH3CH2)3NH+(aq) + NO3-(aq) 2CH3NH3+(aq) + SO42-(aq)