Nitrogen Compounds (1)
advertisement

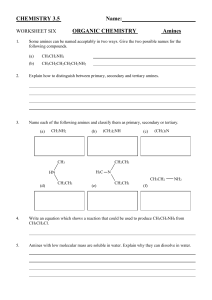
Nitrogen Compounds (1) 1. Organic nitrogen compounds include amines, amides, nitro compounds, nitriles and amino acids. In the spaces below draw ONE example of each of these: Ethylamine Ethanamide Nitrobenzene Ethanonitrile Aminoethanoic acid 2. Name the following: (CH3)2NH CH3(C3H7)NH C2H5(C3H7)NH (CH3)3N Draw phenylamine Draw N,N-dimethylethylamine Describe each of the above as primary, secondary or tertiary amines as required. 3. Draw and explain the shape of an amine of you choice. 4. Why are short chain amines more volatile than similar RMM alcohols? 5. Why are amines soluble in water? 6. Why does the solubility decrease as chain length increases? 7. Why does the volatility of amines decrease with increasing chain length? 8. Amines are bases. What is a base? What structural feature of amines gives them this property? 9. Look at the table on slide 3. Arrange the amines in order of basicity from weakest to strongest. 10. Explain the order. Use the terms positive and negative inductive effect. Does the presence of an amine group on an aromatic ring ACTIVATE or DEACTIVATE the ring? 11. Write an equation for the reaction which takes place when ethylamine dissolves in water. Where does the equilibrium lie? 12.Write an equation for the reaction of ethylamine with hydrochloric acid. Name the product of the reaction. 13. Explain why the smell of the amine disappears unless excess amine is added. 14.Write an equation to explain how adding sodium hydroxide to phenylamonium chloride regenerates the insoluble phenylamine as oily droplets.