Lecture 19
advertisement

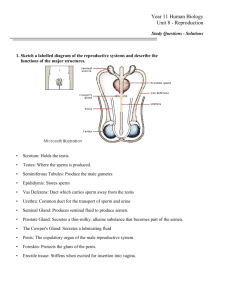
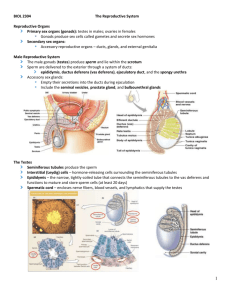
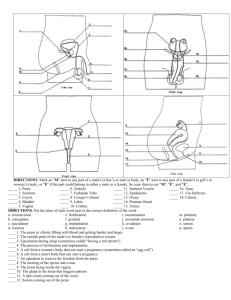
Lecture 19: The Reproductive System I. Overview of Male Reproductive System A. Basic Structures 1. scrotum 2. testes 3. epididymis 4. vas (ductus) deferens 5. ejaculatory ducts 6. accessory glands 7. penis B. Basic Functions 1. production and storage of male gametes (sperm) 2. ability to pass gametes on for procreation II. Male Reproductive Organs A. Scrotum 1. outpouching of abdominal wall - skin and fascia 2. raphe - median ridge separating sides 3. dartos - smooth muscle allowing rise and fall 4. cremaster muscle - skeletal muscle, temp. regulation B. Testes (Testicles) 1. pair of glands that are housed in the scrotum 2. tunica vaginalis - peritoneal continuation envelops 3. tunica albuginea - fibrous tissue, forms lobules 4. seminiferous tubules - produce mature sperm cells 5. sustentacular cells - protect sperm from immune syst 6. interstitial endocrinocytes - secrete testosterone 7. spermatogenesis - process of sperm maturation C. Ducts of the Testis seminiferous tubules l straight tubules l rete testis l efferent ducts l epididymis D. Epididymis 1. curves around the posterior aspect of testis 2. ductus epididymis - tightly coiled tube 3. site of sperm maturation and storage 4. 10 - 14 days for sperm to completely mature 5. stored for up to 4 weeks then destroyed E. Vas (Ductus) Deferens (Seminal Duct) 1. tail of epididymis becomes larger, unconvoluted 2. passes posterior of scrotum, through inguinal canal 3. pseudostratified epithelium & 3 muscle layers 4. stores and moves sperm prior to ejaculation 5. spermatic cord - vessels, nerve, lymph, cremaster 6. inguinal canal - opening for cord above inguinal lig a. deep inguinal ring - aponeurosis trans. abdom. b. superficial inguinal ring - external oblique c. site of most abdominal hernias in men! F. Ejaculatory Ducts 1. union of duct of seminal vesicle & vas deferens 2. along posterior border of bladder G. Urethra 1. final duct of the reproductive & urinary systems 2. prostate -> urogenital diaphragm -> penis 3. prostatic ur. -> membranous ur. -> spongy urethra 4. external urethral orifice - at tip of penis H. Penis 1. body of the penis - main shaft a. corpora cavernosa - dorsolateral parts b. corpus spongiosum - midventral part 2. root of the penis - attached to abdomen a. bulb of penis - base of spongiosum b. crus of penis - base of cavernosa 3. glans penis - bulbous head a. corona - border of glans penis b. prepuce - foreskin I. Accessory Sex Glands - secrete liquid portion of semen 1. seminal vesicles - posterior base of bladder a. fructose rich, alkaline fluid for sperm 2. prostate gland - inferior to urinary bladder a. secretes citric acid and prostaglandins b. site of cancer in men; increases with age 3. cowper's glands - pea sized, below the prostate a. open into the spongy urethra of penis b. secretes lubrication fluid during erection III. Female Reproductive System A. Overview of Female Organs 1. ovaries 2. Fallopian (uterine) tubes 3. uterus 4. vagina 5. vulva 6. perineum 7. mammary glands B. Ovaries 1. upper pelvic cavity, either side of uterus 2. mesovarium - fold of peritoneum, hold in place 3. ovarian ligament - anchor to the uterus 4. suspensory ligament - anchor to pelvic wall 5. hilus - vessels, nerves, lymph 6. Histology of Ovaries a. germinal epithelium - covers surface b. tunica albuginea - connective tissue c. stroma - 2 layered connective tissue i. cortex - outer with ovarian follicles ii. medulla - inner loose layer d. ovarian follicles - developing ova (eggs) e. vesicular follicle - secretes estrogen f. corpus luteum - develops prior to ovulation i. progesterone, estrogen, relaxin, inhibin C. Uterine (Fallopian) Tubes (oviducts) 1. transport ova from ovary to uterus after ovulation 2. positioned between broad ligaments of uterus 3. infundibulum - funnel like end, catches ova 4. fimbriae - fingerlike projections that move ova 5. ampulla - major portion of tube 6. isthmus - short portion attached to uterus 7. Histology of Uterine Tube a. mucosa - internal ciliated columnar epithelium b. muscularis - 2 layers of smooth muscle c. serosa - outer layer, serous membrane D. Uterus 1. located between urinary bladder and rectum 2. fundus - dome shaped top 3. body - funnel shaped central region 4. cervix - narrow opening into the vagina 5. isthmus - between body and cervix 6. uterine cavity - space in the uterus 7. cervical canal - hole surrounded by cervix a. internal ox - junction of isthmus & canal b. external ox - junction of cervix & vagina 8. broad ligaments - peritoneum attaches to cavity a. uterine vessels and nerves pass through 9. uterosacral ligaments - attach to the sacrum 10. cardinal ligaments - hold uterus in position a. carry uterine vessels 11. round ligaments - attach to labia majora 12. uterine and arcuate arteries 13. Histology of Uterus a. perimetrium - outermost layer i. vesicouterine pouch - anterior ii. rectouterine pouch - posterior b. myometrium - thick smooth muscle layer c. endometrium - innermost layer i. stratum functionalis - shed during cycle ii. stratum basalis - permanent layer E. Vagina 1. between the bladder and the rectum 2. fornix - recess superiorly, near the cervix 3. vaginal orifice - opening to outside 4. hymen - vascularized mucus membrane 5. Histology of Vagina a. mucosa - stratified squamous with rugae b. muscularis - smooth muscle, can stretch c. serosa - outermost layer F. Vulva (pudendum) 1. external genitalia 2. mons pubis - thick adipose layer over symphysis pub. 3. labia majora - outer folds of skin 4. labia minora - inside folds 5. clitoris - anterior junction of labia minora 6. prepuce - fold of skin over clitoris 7. glans - exposed portion of the clitoris 8. vestibule - cleft between labia minora 9. bulb of vestibule - masses of erectile tissue 10. urethral orifice - exit of urethra, anterior 11. paraurethral glands - secrete mucus 12. greater vestibular glands - lubrication G. Perineum (both male and female) 1. diamond shaped area of crotch - symph pub -> coccyx 2. line between ischial tuberosities a. urogenital triangle (anterior) b. anal triangle (posterior) H. Mammary Glands 1. modified sweat glands above pectoralis major 2. 15-20 lobes separated by fat tissue 3. lobules - substructure of lobes with alveoli 4. alveoli - milk producing cells, in clusters 5. alveoli -> secondary tubules -> mammary ducts 6. lactiferous sinuses - site of milk storage 7. lactiferous ducts - transport milk to the nipple 8. areola - pigmented area around nipple 9. suspensory (Coopers) ligaments - support breast