Reproduction I. General Terminology 1. Gamete – sex cell a. Ovum
advertisement

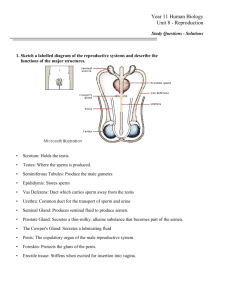
Reproduction I. General Terminology 1. Gamete – sex cell a. Ovum – female Ooycte (oo = egg, cyte = cell) b. Sperm – male 2. Gonads - where gametes are produced a. Ovaries – female b. Testes – male 3. Copulate – sexual intercourse 4. Ejaculation (“to throw or hurl out”) – release of semen 5. Gestation – length of pregnancy 6. Parturition – labor; delivery 7. Intromission – insertion of the penis into the vagina II. Female organs 1. Vulva – opening into the female a. vagina – canal from the vulva to the cervix b. labia (lips) c. Vestibular glands (seen in cows, cats, and some sheep) – secrete mucus to lubricate the vagina d. Clitoris – erectile tissue in the female (similar to the glans penis of themale) 2. Cervix (neck) – canal to the uterus 3. Uterus a. body – muscular wall; endometrium is the inner lining b. uterine horns (fallopian tubes, oviduct) – tubes that connect the uterine body to the ovaries animals that have multiple babies at one time have long horns and a short body horses have short horns and a large body similar to humans cows and sheep have long horns and short body c. Ovaries – egg development 4. Broad ligaments – contain blood vessels and nerve fibers that supply the ovaries, horns, and uterus; supports the uterine body 5. Suspensory ligaments – attachment of the ovary to the body wall 6. Follicle – cyst like structure on the surface of the ovary while the egg is developing; produces LH to cause egg maturity 7. Corpus Luteum (CL) – ruptured follicle that fills up with a yellow substance; secretes progesterone. 8. Caruncles – circular thickening of the ruminant’s inner lining of the uterine body; attachment site of the placenta 9. Cotyledon – site of connection at the caruncle and fetus 10. Placenta- sac that joins mom and baby; exchange of nutrients, oxygen, and waste products III. Copulation 1. Induced Ovulators (rabbits, cats, ferrets, camelids) – females have to be stimulated by the male’s spines on their penis. 2. “Tie” - after ejaculation in dogs, the bulb of glans swells and the dog is unable to retract; last 15-20 minutes. 3. Typical breeding – sperm travel up to the uterine body or horn to meet the egg. Once fertilization takes, the egg will embed itself in the uterine lining. IV. Hormones/Estrous Cycle 1. Proestrus – beginning of the sexual season a. FSH increase (Follicle stimulating hormone) – comes from the pituitary gland and cause egg maturation b. B. Estrogen increases – prepares the female physicall and mentally for copulation 2. Estrus – “heat cycle” sexual receptivity a. FSH and Estrogen decreases b. LH increase (Luteinizing hormone) – comes from the pituitary gland and promotes ovulation 3. Metestrus – after ovulation it is a short period where the CL develops 4. Diestrus – pregnancy a. Progesterone increases - maintains pregnancy 5. Anestrus – silent period V. Reproductive Table Species Estrus Duration/Frequency Gestation Dog 9 days/4-9 months 63 days Cat Induced ovulator 63 days Horse 5-6 days/ Spring-Fall monthly 11 months Cows 18 hours/Spring – Fall monthly 9 months Sheep 24-36 hours/Spring – Fall monthly 5 months Goats 24-36 hours/ Spring – Fall monthly 5 months Pigs 48-72 hours/ Spring – Fall monthly 3 months, 3 weeks, 3 days Rabbits Induced ovulator 32 days Guinea Pigs 1-6 hours/ 15-17 days 63 days Ferrets March-September 44 days 111 days Chinchillas Rats/Mice 14 hours/4-5 days 21 days Hamsters 14 hours/4-6 days 16 days Gerbils 14 hours/4-6 days 22-24 days Llamas/Alpacas Induced ovulator 11 months Sugar Gliders 2 days/28 days 16 days prior to fetal migration VI. Male Reproductive Organs 1. Scrotum (scrotal sac) – external pouch that holds the testes; keeps the testes at a lower body temperature for sperm development 2. Testes (Testicles) – where sperm are developed and testosterone is released; in utero the testes develop in the abdominal cavity near the kidney and then slowly drop down prior to sexual maturity a. Seminiferous Tubules – cells that produce the sperm b. Epididymis – where the sperm are stored after they are mature c. Vaginal Tunic – connective tissue that surrounds the testes, scrotum, cord d. Cremaster muscle – muscle that attaches to the scrotum/body; it adjusts the position of the testes according to the body temperature 3. Spermatic cord – has blood vessels, nerves, lymphatic vessels, Vas Deferens; connects testes to the prostate gland 4. Vas Deferens – carries the sperm to the prostate gland 5. Seminal Vesicles – glands that open into the Vas Deferens where it joins the urethra to provide nourishment to the sperm and adds volume to the semen. Dogs and cats do not have one. 6. Prostate Gland – aids in sperm motility during ejaculation 7. Bulbourethral gland – gland on either side of the urethra; secretes a lubricant for sperm (in humans it is called the Cowper’s gland); dog’s don’t have one 8. Urethra – tube that connects the prostate/bladder to the penis 9. Penis a. Sigmoid Flexure – S shaped penis in ruminants and pigs 10. Os penis – bone encased in the penile tissue; most species other than dog and ferret have a cranioventral one 11. Prepuce – retractable fold of skin covering the glans penis (foreskin) 12. Bulb of the glans – erectile tissue located in the rear of the penis; enlarges at the end of the ejaculation to form the tie in dogs VII. Semen Analysis A. Spermatozoa 1. head – nucleus 2. Midpiece - power plant 3. Tail – movement B. To determine fertility 1. count 2. motility 3. Shape VIII. Collection Semen for AI or semen analysis 1. Electroejaculator - involves applying a series of short, low-voltage pulses of current to the pelvic nerves which are involved in the ejaculatory response. Commonly used in bulls 2. Manual stimulation - Many males can be induced to ejaculate by applying pressure and massage to the penis. After the male becomes aroused, an artificial vagina is slipped over the penis to facilitate harvesting the semen. This technique is commonly used for collecting semen from pigs and dogs 3. Mount a dummy 4. Redirection from a receptive female X. Vocabulary 1. Flehmen – males response with the upper lip curling up when near a female in heat 2. Vaginitis – inflammation of the vaginal area 3. Amniotic fluid – the fluid that surrounds the fetus in the placenta 4. Mammary – breast 5. Lactation – production of milk 6. Dystocia (dys = difficult, tocia = birth) – difficult birth 7. Orifice – opening 8. Embryo – fertilized ovum 9. Orchidectomy (Orchid = testicle, ectomy = remove) – castration/neuter 10. Cryptorchid (Crypt = hidden) – retained testicle 11. Prostatis – inflammation of the prostrate gland 12. Epididymitis – inflammation of the epididymis 13. Castration – surgical removal of the testicles 14. Ovarian hysterectomy – surgical removal of the uterus and ovaries (spay) XI. Pathological conditions 1. Adenocarcinoma of the prostate – malignant tumor of the prostate 2. Testicular carcinoma – malignant tumor of the testes 3. Trichomoniasis – parasite in bulls that can cause infertility 4. Testicular degeneration – due to heat or injury testes get smaller 5. Broken penis – due to trauma; especially during A.I. or collection 6. Teaser Bulls – surgically altered bulls incapable of natural insemination used to detect females in heat 7. Bean – smegma and debri that becomes trapped in the urethra of the horse 8. Eclampsia – (Milk Fever) decreased Ca concentrations; associated with dystocia or large litters 9. Pyometra – bacterial infection inside the uterus; causes the uterus to swell with pus a. Open pyometera – pus leaking out the vagina b. closed pyometera – no obvious infection 10. Metritis – inflammation of the uterus 11. Uterine prolapsed – uterus prolapsed out the vagina; associated with large babies 12. Uterine torsion – twisting of the uterus 13. Windsucker – defect in the mare where the vaginal opening is deeply located and the lips of the vulva don’t close properly. A caslicks surgery is done to close up the upper vulvar fold to prevent contamination. This needs to be removed prior to parturition. 14. Retained placenta 15. Hermaphrodite – genital tract of both sexes 16. Freemartin – female cow that was a twin with a male cow and has a defective genital tract 17. Pseudopregnancy