Reproductive
advertisement
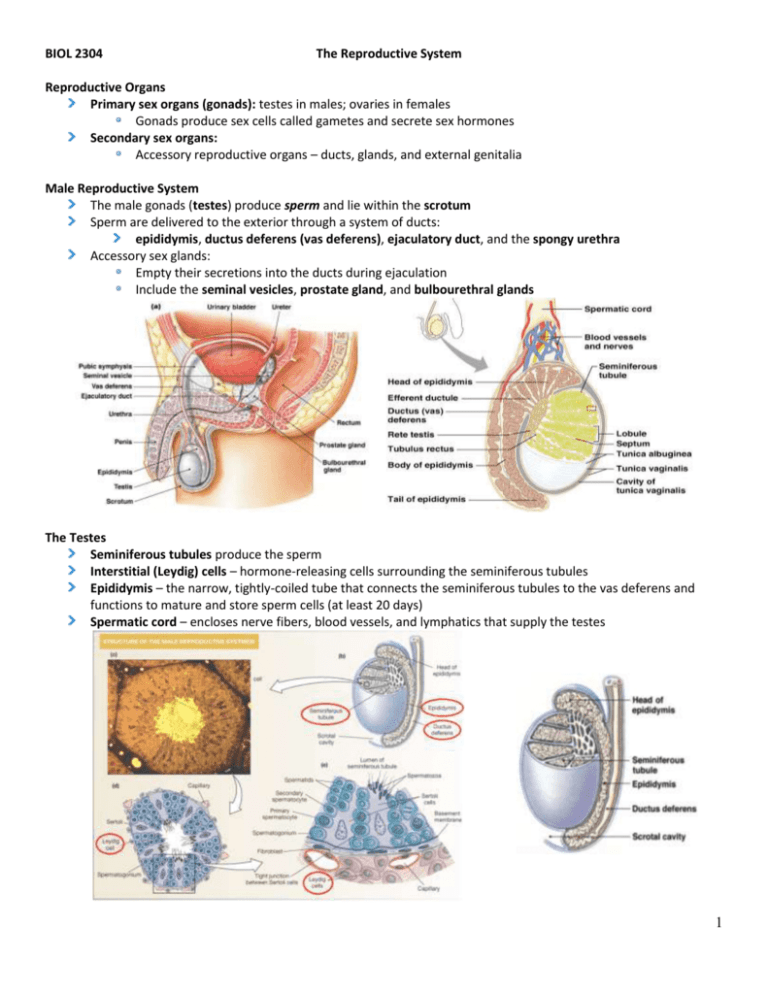
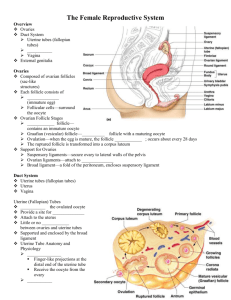
BIOL 2304 The Reproductive System Reproductive Organs Primary sex organs (gonads): testes in males; ovaries in females Gonads produce sex cells called gametes and secrete sex hormones Secondary sex organs: Accessory reproductive organs – ducts, glands, and external genitalia Male Reproductive System The male gonads (testes) produce sperm and lie within the scrotum Sperm are delivered to the exterior through a system of ducts: epididymis, ductus deferens (vas deferens), ejaculatory duct, and the spongy urethra Accessory sex glands: Empty their secretions into the ducts during ejaculation Include the seminal vesicles, prostate gland, and bulbourethral glands The Testes Seminiferous tubules produce the sperm Interstitial (Leydig) cells – hormone-releasing cells surrounding the seminiferous tubules Epididymis – the narrow, tightly-coiled tube that connects the seminiferous tubules to the vas deferens and functions to mature and store sperm cells (at least 20 days) Spermatic cord – encloses nerve fibers, blood vessels, and lymphatics that supply the testes 1 The Scrotum Contains paired testicles that hangs outside the abdominopelvic cavity External positioning keeps testes 3C lower than core body temperature, needed for sperm production Intrascrotal temperature kept constant by two different muscles: Dartos muscle – smooth muscle that wrinkles scrotal skin Cremaster muscle – bands of skeletal muscle that elevate the testes The Penis Urethra – conveys both urine and semen (at different times) Three cylindrical bodies of erectile tissue in shaft of penis: One corpus spongiosum and two corpora cavernosa: Expansion of the corpora cavernosa compresses drainage veins and retards blood outflow and maintains engorgement The corpus spongiosum functions in keeping the urethra open during ejaculation Glans penis – the expanded tip of the penis that surrounds the urethral opening; continuous with the corpus spongiosum Prepuce (aka “foreskin”) – a lose fold of skin that surrounds the glans penis; secretes a waxy material called smegma 2 Accessory Glands: Seminal Vesicles Seminal Vesicles – secrete a viscous alkaline fluid that accounts for 60% of the volume of semen and which contains nutrients and enzymes Seminal vesicles join the ductus deferens to form the ejaculatory duct where sperm and seminal fluid mix Accessory Glands: Prostate Gland Prostate gland – the gland that encircles part of the urethra inferior to the bladder Produces a milky, slightly acid fluid that accounts for one-third of the semen volume and which contains nutrients, enzymes, and antibiotics Accessory Glands: Bulbourethral Glands (Cowper’s Glands) Bulbourethral Glands – pea-sized glands inferior to the prostate Produce thick, clear mucus prior to ejaculation that neutralizes traces of acidic urine in the urethra Sperm Conveyance From seminiferous tubules, the sperm enter the epididymis Upon ejaculation the epididymis contracts, expelling sperm into the ductus deferens Ductus deferens merges with the duct of the seminal vesicle to form the ejaculatory duct From ejaculatory duct, sperm enter urethra 3 Female Reproductive System Ovaries are the primary female reproductive organs Make female gametes (ova) Secrete female sex hormones (estrogen and progesterone) Internal genitalia – ovaries, uterine tubes, uterus, vagina External genitalia – vulva, clitoris, labia, and hymen Ovaries Embedded in the ovary cortex are ovarian follicles Each follicle consists of an immature egg called an oocyte Ovaries Primordial follicle – one layer of squamous-like follicle cells surrounds the oocyte Primary follicle – two or more layers of cuboidal granulosa cells enclose the oocyte Secondary follicle Tertiary follicle (aka vesicular or Graafian follicle) – at its most mature stage, cell bulges from the surface of the ovary Ovulation – the ejection of the oocyte from a mature vesicular follicle Corpus luteum – a ruptured follicle after ovulation Zona pellucida – the thick transparent membrane surrounding the ovum before implantation Corona radiata – the layer of cells immediately surrounding the ovum 4 Ovaries and Oocytes 5 Uterine Tubes (Fallopian Tubes) Uterine tubes – receive the ovulated oocyte and provide a site for fertilization; have direct physical contact with the ovaries Fimbriae of the uterine tube – beating cilia at end of uterine tubes that create currents to draw the oocyte into the uterine tube Infundibulum of the uterine tube – the portion between the ampulla and fimbriae Ampulla of the uterine tube – the dilated portion of uterine tube which curves over the ovary Uterus Uterus – a hollow, thick-walled organ that receives, retains, and nourishes the fertilized egg Body of the uterus – the main, central portion of the uterus Fundus of the uterus – the rounded region superior to the entrance of the uterine tubes Cervix of the uterus – the narrow outlet that protrudes into the vagina Cervix Cervical canal – the canal extending from the uterus to the vagina Internal os – the opening at the top of the cervical canal External os – the opening at the bottom of the cervical canal Uterine Wall Composed of three layers: Perimetrium – outermost serous layer; the visceral peritoneum Myometrium – middle layer; interlacing layers of smooth muscle, during labor this layer contracts to expel fetus Endometrium – mucosal lining of the uterine cavity The inner layer of the uterus Allows for implantation of a fertilized egg Sloughs off if no pregnancy occurs (menses) 6 Vagina Thin-walled tube lying between the bladder and the rectum, extending from the cervix to the exterior of the body Serves as the female organ of copulation; receives the penis during sexual intercourse Provides a passageway for birth and menstrual flow Vulva Mons pubis – mound of fatty tissue overlying the pubic symphysis (pubic bone) Labia majora – outer folds of skin contains fat, sudoriferous and sebaceous glands, covered with pubic hair (homologous to scrotum) Labia minora – inner folds of skin containing sebaceous glands and nerve endings that provide stimulation Clitoris – cylindrical mass of erectile tissue covered by a layer of skin called the prepuce (homologous to penis) Vestibule – cleft between the labia minora; includes the urethral orifice, vaginal orifice, and vestibular glands that produce lubricants during sexual intercourse Urethra – muscular tube, opening is anterior to opening of vagina, carries urine from bladder to exterior 7 Mammary Glands Modified sweat glands consisting of 15-25 lobes that radiate around and open at the nipple Lobes contain glandular alveoli that produce milk in lactating women 8