2006 10 27 CHEM 2302 Assignment 4 (IC) for students
advertisement

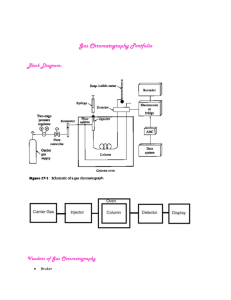
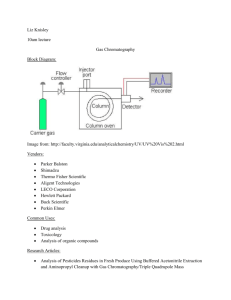
2006 10 27 CHEM 2302* Assignment 4 Ion Chromatography 1. Draw a block diagram to show the instrumentation of ion chromatography. 2. What is the working principle of ion chromatography? Is retention based on attraction or elution? 3. Why would the semiconductor industry need ion chromatography? 4. Potassium is a vital mineral necessary for proper cell metabolism. Deficiencies are found in patients who are prescribed diuretics (kidney stimulants) for hypertension or heart disease. If a patient takes massive supplements, toxic amounts of potassium may saturate the body's cells. Is it possible to determine K levels in blood serum by DPASV or ion chromatography? 5. What are ion-exchange resin particles made of? 6. Can you use resins with tertiary ammonium groups (Resin-NR'2H) as strong cation or anion exchangers? 7. What is the difference in performance between strong and weak exchanger resins? Would this affect the elution order (or selectivity) of analyte ions? 8. What is ion chromatography useful and NOT useful for? 9. Has the U.S. EPA approved the use of ion chromatography for drinking water monitoring of secondary contaminants, Cl- and SO42-? 10. In ion chromatography, can you predict the elution order of F-, Cl-, SO4= and NO3-? 11. Bonus question 12. What are good eluents for anion chromatography? Which eluent is the strongest among Na2CO3, NaHCO3, NaI and NaOH when these aqueous solutions are used at equal molar concentrations? 13. Are NaHCO3/Na2CO3 eluents useful for anion or cation chromatography? 14. Can ion chromatography determine both inorganic and organic anions in the same run? Explain why or why not. 15. Why is it important to determine strontium in toothpaste by ion chromatography? Is ethylene diamine a good eluent for cation chromatography? 16. Why is it important to monitor the concentration of citrate in soft drink formulations? How can you make the citrate ion peak come out on the chromatogram in less than 4 minutes? 17. The exchange capacity of an anion column was measured by washing extensively with 1.0 M NaOH and H2O. 200 mL of 1.0 M NaCl was next passed through the column, and the eluate was collected. Titration of the eluate with 0.010 M HCl required 10.7 mL to reach the end point. If the column contained 25.0 g of resin, calculate the exchange capacity of the resin (as the number of micromoles of charged sites per gram of resin). 18. What kind of detector is most commonly used for monitoring the IC separation of cations and anions? Why would it be necessary to use a suppressor device before the detector? 19. Design an auto-suppression scheme for the cation chromatography of KCl and CaCl2, using HCl as the eluent. 20. Bonus question Draw a diagram to explain how the conductive eluent ions H+ and MSA- (where MSA = methanesulfonate) can effectively be removed from the eluent using an autosuppressor device in cation chromatography. 21. What is the working principle of conductivity detection for ion chromatography? 22. Why is suppressed-conductivity important to ion chromatography? 23. How does an auto-suppression device (or self-regenerating suppressor) enhance signal-to-noise ratio to improve detection limits? 24. Water is used as a regenerant in the self-regenerating suppressor for auto-suppression. What does it do? 25. How can analyte conductivity be enhanced? 26. For the separation of Mg2+, Ca2+, Li+, Na+, NH4+ and K+ by ion chromatography, can the eluent be a solution of ethylenediammonium salts (+H3NCH2CH2NH3+)? 27. How would you use the ionic strength of eluent as a variable parameter to control ion chromatography? 28. By changing the eluent pH in the range of 2-8, can one adjust the retention times of I-, NO3-, SO42-, HPO42- and citrate? 29. Consider a protein with a net negative charge that is tightly adsorbed on an anion-exchange column at pH 8. What would be a useful eluent gradient for eluting the protein?