Periodic Trends Summary Chart with Fill
advertisement
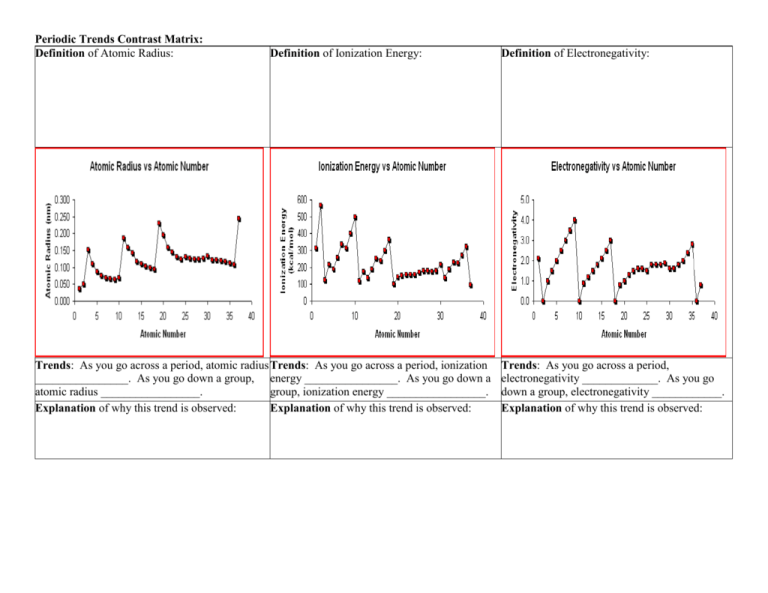
Periodic Trends Contrast Matrix: Definition of Atomic Radius: Definition of Ionization Energy: Trends: As you go across a period, atomic radius Trends: As you go across a period, ionization ________________. As you go down a group, energy ________________. As you go down a atomic radius _________________. group, ionization energy _________________. Explanation of why this trend is observed: Explanation of why this trend is observed: Definition of Electronegativity: Trends: As you go across a period, electronegativity _____________. As you go down a group, electronegativity ____________. Explanation of why this trend is observed: Arrows showing how trend increases: Arrows showing how trend increases: Arrows showing how trend increases: Periodic Trends Contrast Matrix Answers: Definition of Atomic Radius: The atomic radius of an element is half of the distance between the centers of two atoms of that element that are just touching each other Trends: As you go across a period, atomic radius decreases. As you go down a group, atomic radius increases. Explanation of why this trend is observed: Increasing the number of protons increases the nuclear charge in the nucleus in the same principal energy level (n). This increased charge increases attraction of electrons to the nucleus. As you go down a group, adding another principal energy level results in valence electrons being further from the nucleus. Arrows showing how trend increases: Definition of Ionization Energy: The ionization energy, is the energy required to completely remove an electron from a gaseous atom or ion. The closer and more tightly bound an electron is to the nucleus, the more difficult it will be to remove, and the higher its ionization energy will be. Trends: As you go across a period, ionization energy increases. As you go down a group, ionization energy decreases. Explanation of why this trend is observed: As you go across a period, the increased nuclear charge decreases the atomic nucleus, making it more difficult to remove an electron. As you go down a group, the ionization energy decreases because the addition of a principal energy level results in the electrons becoming further from the nucleus: decreased attraction makes it easier to remove an electron. Arrows showing how trend increases: Definition of Electronegativity: Electronegativity is a measure of the attraction of an atom for the electrons in a chemical bond. The higher the electronegativity of an atom, the greater its attraction for bonding electrons. Trends: As you go across a period, electronegativity increases. As you go down a group, electronegativity decreases. Explanation of why this trend is observed: Increasing nuclear charge increases attractions to electrons (across a period); as you go down a group, there is an added principal energy level (electrons are further from the nucleus), which makes the electron further from the nucleus, making it more difficult for the atom to attract electrons. Arrows showing how trend increases: