Instructor`s Copy
advertisement

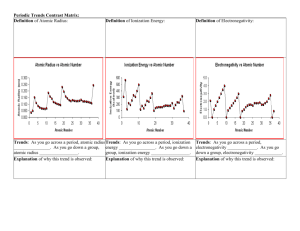
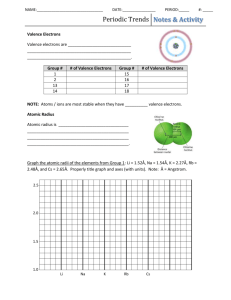
Instructor’s Copy Lab Worksheet – The Latest Trend The data on this table depends on the property assigned. Table 1: Scale data on ________________________________ (which property) Scale information Length of soda straw (cm) 19.6 Half the straw length (cm) 9.8 Largest value of property to be investigated Scale for straw length vs. property (cm):1/2 straw length /largest value of property Property modeled Atomic number (# of protons) # Mass MP BP Dens. Radii Ion Elect 88 226 3620 4200 11.9 280 2372 4.0 .003 .002 .82 .035 .004 2.45 .11 .04 Table 2: Trends on the periodic table Trend down groups Trend from left to right in period Increases going down Increases going right Atomic mass Increases going down Increases going right Melting point Except for hydrogen, decreases going down Increases for first 4, then a major drop with continued decrease Boiling point Except for hydrogen, decreases going down Increases for first 4 then decreases Density Except for sodium, increases going down Atomic radius Increases going down In general, it increases for the first 4, then a major drop with slight increases. Decreases going right until it reaches noble gas, which is bigger Ionization energy Decreases going down Increases going right Electronegativity Decreases going down Increases going right QUESTIONS: 1. What is the trend in atomic number? Using the idea that the atomic number is the number of protons, explain why this trend occurs. The table is set up by increasing # of protons (atomic number). 2. What is atomic mass? Explain why this trend occurs. Atomic mass is the mass of the protons + neutrons. As the # of protons increases, so does the number of neutrons and electrons. This increases the mass. 3. What is the trend in melting and boiling points? Explain why this might occur. Both points decrease going down the groups because the elements 4. What is density? Explain why this trend might occur. Density is the mass/volume of a substance. It tells how tightly packed the atom is. In general, the density increases for the first 4 columns in a period because the mass increases while the volume does not change much. After the first 4, the volume decreases as the electrons are held slightly closer. Going down the group, the density generally increases as a large amount of mass is added to the nucleus. 5. What is atomic radii? Explain why this trend might occur. Half the distance from the center of the nucleus to the outer electrons. Radius increases going down the group as more energy levels are added to the atom. Radius decreases going right because the electrons are held closer to the nucleus as the energy level fills up. 6. What is ionization energy? Explain why this trend is present. Ionization energy is the energy needed to remove the most loosely held electron. This is directly related to radius, it decreases as the radius increases because the electrons are easier to pick off. 7. What is electronegativity? Explain why this trend might occur. A measure of the tendency of an atom to attract a bonding pair of electrons. As the atom gets bigger, it does not attract its own electrons so it cannot pick electrons off another atom. 8. What is the relationship between electronegativity and ionization energy? They are directly related. If the atom can’t hold its electrons to its nucleus, it can’t attract other electrons either. 9. What is the relationship between atomic number and atomic mass? Protons have mass. If the number of protons increases, the mass increases. 10. What is the relationship between atomic radius and other properties on the table. The atomic radius seems to directly affects the ionization energy and the electronegativity because the larger the atom, the less likely it is to hold its own electrons tightly or attract electrons from other atoms.