Gastro32-HistologyAccessoryOrgans
advertisement

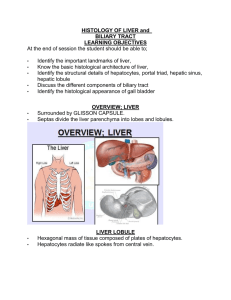
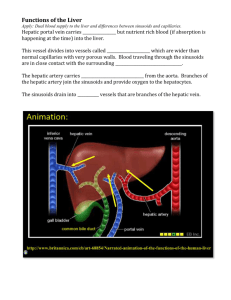
GI #32 Thur 02/27/03 2pm Dr. Wordinger R. Vayani Proscribe Samera Kasim Page 1 of 5 Histology: Accessory Organs Liver, Gall Bladder and Exocrine Pancreas --Liver-I. Functions of the liver a. The liver has 2 main functions: i. Exocrine 1. Includes synthesis and secretion of bile via the duct system ii. Endocrine 1. Includes synth and secretion of plasma proteins, cholesterol, lipoproteins and glucose to the bloodstream b. Another function of the liver is detoxification of lipid soluble drugs, breakdown of steroid hormones, glycogen storage and urea production. i. Steroid hormones include estrogen, progesterone and testosterone ii. Accomplished by the work of hepatocytes, the fundamental cell of the liver II. Lobules a. Hepatocytes make up the bulk of the liver b. Connective tissue (CT) is a minor component c. When looking at a slide of the liver, there are 3 ways to analyze its function. Different shapes can be drawn onto the slide, each emphasizing a different function, namely its endocrine, exocrine and metabolic functions d. They are as follows: e. Classic lobules (see “classic liver lobule” in the study guide handout) i. Emphasizes the endocrine function of the liver because the central v. is at the center of the lobule ii. Shaped like hexagonal cylinders iii. Hepatocytes are radially arranged in plates around small venules (the central vein) iv. The corners of the hexagon are portal triads 1. triads include a branch of: a. hepatic a. b. portal v. (interlobular v) c. bile duct (interlobular bile duct) v. because the liver is supplied by both the hepatic a. and the portal v., it is said to have dual blood supply. f. Portal lobules i. Emphasizes the exocrine function of the liver because the interlobular bile duct is at the center of each lobule. ii. Bile flows: bile canaliculi terminal ductules interlobular bile duct Right and Left hepatic ducts cystic duct common bile duct. iii. Bile flows in the opposite direction of blood flow (which serves the endocrine function of the liver) GI #32 Thur 02/27/03 2pm Dr. Wordinger R. Vayani Proscribe Samera Kasim Page 2 of 5 iv. Bile canaliculi are formed by tight juctions between hepatocytes, but are not lined by a specialized cell layer. 1. the tight junctions keep fluids from going into the sinusoids g. liver acinus (Rappaport lobules) i. diamond shaped ii. the liver acinus emphasizes metabolic gradients and the functional activity of the liver iii. corners of the diamonds are formed by 2 central vv. and two portal triads. iv. Each acinus has 3 zones as determined by gradation of blood supply: 1. Zone 1 a. Near center b. Receives blood first from terminal distributing vessels c. Thus receives most of the glucose/nutrients d. Higher glycogen storage e. Last cells to die f. First to regenerate g. Higher oxygen levels h. First to be overloaded by toxins that come through the liver i. Have the greatest mitotic activity after toxins introduced to the kidney 2. Zone 2 a. Less active than Zone 1 b. Lipid and aging pigments found 3. Zone 3 a. Same as Zone 2 III. Sinusoids of the liver a. The blood vessels between the cords of hepatocytes are lined by a discontinuous, fenestrated layer composed of: i. Typical intimal vascular cells ii. Kupffer cells which phagocytose damaged RBC that are not removed by the spleen (or in the event of an injured spleen) 1. derived from monocytes 2. may contribute to endothelial lining or just rest on the lining in the lumen of the sinusoid b. Space of Disse i. An extracellular space between the sinusoids and the hepatic cells ii. Site of traffic of materials between hepatocytes and the lumen of the sinusoids iii. Particles that are too large may be stopped from passing through IV. Hepatocytes a. The ONE cell of the liver GI #32 Thur 02/27/03 2pm Dr. Wordinger R. Vayani Proscribe Samera Kasim Page 3 of 5 b. Diverse functions c. Polyhedral cells with 3 surfaces i. One exposed to space of Disse ii. One exposed to canaliculus iii. One adjacent hepatocytes d. Products can be directed to the various borders e. Have lots of organelles with many functions: i. RER synthesizes plasma proteins and the protein portion of lipoproteins ii. GOGLI appareatus is always present at the pole of the cell that form the bile canaliculus iii. SER is used for: 1. drug detox 2. steroid hormone breakdown 3. conjugation of bilirubin before it’s excreted to bile 4. VLDL synth 5. cholesterol synth 6. enzymatic conversion of the inactive form of glycogen synthase into the active form --gallbladder-V. Gallbladder structure a. A diverticulum of the common hepatic duct b. 3 inches long, 1.5 inches wide c. can undergo considerable distension d. the wall only has 3 layers: there is NO SUBMUCOSA i. mucosal layer: 1. has folds that are branched 2. simple columnar epithelium with apical microvilli and basal nuclei 3. Sodium pump n the basal membranes to facilitate water absorption from stored bile ii. Muscularis externa 1. smooth mm under the lamina propria of the mucosal layer 2. (REMEMBER: there’s not a submucosa!!) 3. muscle fibers respond to CCK iii. Adventitia/Serosal layer 1. has BOTH 2. adventitia covers the part attached to the liver 3. serosa covers its free surface VI. function a. Absorb water b. Store bile produced in the liver c. Concentrate the bile GI #32 Thur 02/27/03 2pm Dr. Wordinger R. Vayani Proscribe Samera Kasim Page 4 of 5 d. As mentioned above, CCK is a hormone that stimulates contraction of smooth mm of the gallbladder. Remember that CCK is produced by enteroendocrine cells of the small intestines in response to ingested fats. --exocrine pancreas-VII. Structure a. Overall the pancreas is a Lobulated, compound tubuloalveolar gland that has both endocrine and exocrine function. i. The endocrine functions are carried out by the islet of langerhan b. The acini or alveoli of the pancreas are tubular shaped and surrounded by a basal lamina c. They are composed of 5-8 pyramidal cells arranged around a central lumen d. The lumen may have centroacinar cells i. These are the cells of the duct system ii. In the absence of islet cells, these are the only way that you would be able to determine pancreatic exocrine cells apart from parotid gland cells. They look very similar. VIII. The duct system a. The pancreas does not have striated ducts i. This is the other way that you may be able to distinguish the pancreas from the parotid gland. b. There are intercalated ducts i. Lined by low cuboidal epithelium ii. Extend into the lumen of the alveolus as centroacinar cells c. Merge into the main excretory duct IX. Secretions a. Acini make serous secretions that are released into the intercalated ducts b. Stimulated to secrete products by CCK c. Cells of the intercalated ducts are stimulated to secrete their products by secretin (from the small intestine) Notes: -Lipid Absorption material will be covered by Gwirtz. -the histo slides that were used during lecture were mainly from the study guide. Below are additional comments made about each slide or items that you should be able to notice: Liver: Liver-low mag o Delineations of the lobules are by connective tissue o The “matrix” is composed of hepatocytes and blood vessels Liver lobule – Central Vein o Blood flows from the periphery through the sinusoids to the central vein Liver sinusoids GI #32 Thur 02/27/03 2pm Dr. Wordinger R. Vayani Proscribe Samera Kasim Page 5 of 5 Gallbladder o Each of the nuclei on the slide is a hepatocyte o Notice that they are surrounded by vascular supply Portal triads o Know the content of the triad o They’re at the periphery of the classic lobule o The bile duct (BD) has simple columnar/cuboidal) epithelium Thus you can distinguish it from a vascular vessel which would have simple squamous epith. Classic liver lobule o Endocrine function o Hexagon Portal liver lobule o Exocrine function o Bile duct in the center Acinar liver lobule o Metabolic function: Glycogen breakdown and glucose production o Corner consist of portal triads on the Right and Left and central veins at the top and bottom the diamond o Zone 1 is near the center. o Blood flow occurs in the direction along the line depicted from the portal triad to the central vein Liver sinusoids – phagocytosis (2nd to last slide) o This demonstrates an experiment done with a cat. o Ink particles were injected to the cat o They are being phagocytozed by Kupffer cells Liver sinusoids – phagocytosis (last slide) o Notice that the nuclei of the Kupffer cells are flattened o They nuclei of the hepatocytes are more rounded. First 2 slides: o The projections that protrude into the lumen are NOT villi, but are folds Surface epithelium o Simple columnar Pancreas Pancreas – endocrine and exocrine o The exocrine pancreas surrounds the endocrine (the islet cells grouped together in the center) Exocrine Pancreas o Notice there are no islet cells present o This closely resembles the parotid salivary gland Last 2 slides: o Notice the centroacinar cells: the distinguishing feature compared to the parotid gland