Collision Theory and Reaction Rates
advertisement

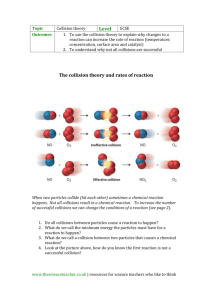
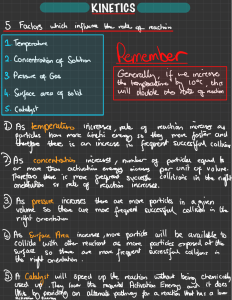
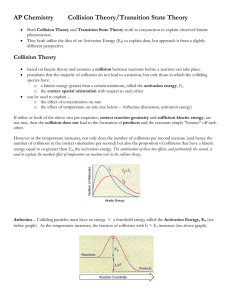
Collision Theory and Reaction Rates Collision theory: chemical reactions occur only if energy is provided to break bonds. The source of that energy is the kinetic energy of the molecules. Concepts of collision theory: 1. Particles are in constant random motion. Kinetic energy is proportional to the temperature of the sample. 2. Chemical reactions MUST involve collisions between particles 3. Effective collisions have sufficient energy and correct orientation to break bonds… ineffective collisions result in no change/ “rebound” 4. Reaction rate depends on the frequency of collisions (can be increased by increasing concentration, surface area or temperature) and on the fraction of collisions that are effective. Activation energy: (Eact) -aka activation energy barrier -is the minimum energy with which particles must collide before they can Re-arrange in structure to have an effective collision. Diagram: **changing the nature of the reactants or using a catalyst changes the size of the barrier** Reaction Progress diagram for Endothermic reactions: Reaction progress diagram from Exothermic reactions