MID-TERM EXAM
advertisement

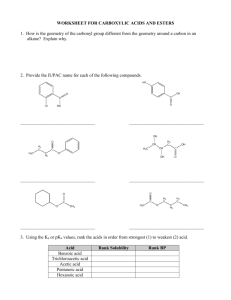
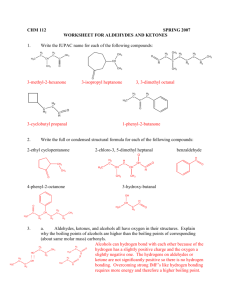
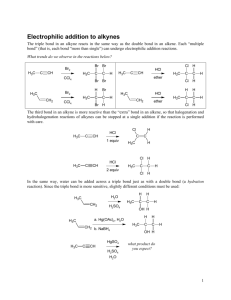
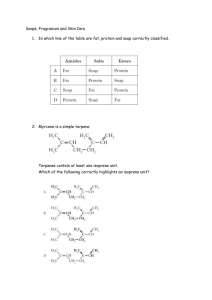
CHM 112 GAGE SPRING 2002 NAME _____________________________ DATE _____________________________ MID-TERM EXAM 1. Write the name for each of the following compounds: (24) CH 3 H2 C C H3C CH H2C Cl O CH 3 C H2 C Cl CH 2 H2 C H3C H2 C C N H CH 3 C H2 H3C CH 2 O C H2 H N-ethyl pentanamide H3C H2 C C C H2 C H2 4-cyclohexyl butanal 3, 7-dichloro-3, 6, 6-trimethyl decane O CH 3 H2 C H3C O C O Br C CH 3 CH 3 H3C C H2 CH 3 H2 C C O CH 3 3-chloro-4-heptanone O CH CH Cl 3-bromo benzoic acid CH3 H2 C C OH ethyl t-butyl ether H3C H2 C H H 3C H2 C C C C H2 CH 3 CH 2 isopropyl methanoate 2. a. H 3C 3-ethyl-4-methyl-3-heptene A benzene ring has three double bonds. Can it undergo addition? Explain why or why not. (5) Benzene will not undergo addition because the electrons in the double bonds are “delocalized”. Since they do not reside between two specific carbons all the time, it is harder to commandeer those electrons to use in making additional bonds on two adjacent carbons. b. Why would an acid or amine functional group on a compound be converted to the salt form before being used in a medication? (5) The salt form of an acid or amine contains an ionically bonded region. These compounds will be much more soluble in water because of stronger ion-dipole forces that form with water rather than the dipole-dipole forces. 1 c. 3. Which has a higher energy, a single carbon-carbon bond or a double carbon-carbon bond. Explain your answer. (5) The C-C double bond will be higher energy because there is greater repulsion with two pairs of electrons between two carbon nuclei than with one pair. This generates a higher energy state to maintain the bond. Write the full or condensed structural formula for each of the following compounds. (24) acetone N-methyl-N-isopropyl aniline 4-ethyl toluene CH 3 O C H3C CH 3 CH3 N CH H3C CH 3 CH 2 H 3C pentyl heptanoate 3, 4-dimethyl-2-octene benzaldehyde CH 3 H2 C H3 C H2 C C H2 H2 C O C H2 H2 C C C H2 H2 C C H2 CH 3 C H2 H C H3C O H2 C CH C CH 3 C H2 C H2 O C CH 3 H 3, 5-dibromocyclohexanol 2, 4-diiodo-3-hexanone I I OH CH H 3C CH C O Br Br 2 CH 3 C H2 4. Matching: match the compound in COLUMN B with the type of reaction it can undergo COLUMN A. There may be more than one choice for each reaction. To receive full credit you need to list all possible compounds for each reaction type. (20) COLUMN A COLUMN B __C, K_______ hydrolysis A. 2-methyl-2-butanol __B, E, I_______ addition B. butanone __A, D, F, G, J_ condensation C. methyl butanoate ___G, A_______ elimination D. butyl amine ___E, G______ oxidation E. butanal ___B, E, F____ reduction F. benzoic acid ___C________ saponification G. 2-butanol ___D, F______ neutralization H. methoxy propane I. 3-hexyne J. phenol K. butanamide 5. For each of the pairs below, provide a simple test that will distinguish between the two compounds. Indicate what you would expect to see if you performed the test. (12) a. cyclohexanol and 2-methyl-2-butanol You can add K2Cr2O7 or KMnO4. The cyclohexanol will be oxidized to cyclohexanone and there will be a color change from yellow to green or purple to brown. There will be no change with the tertiary alcohol. b. hexanal and methyl pentanoate You can add K2Cr2O7 or KMnO4, Cu2+ or Ag[NH3]+. The hexanal will react positively (yellow to green, purple to brown, blue to red solid or silver mirror). There should be no reaction with the ester. c. cyclohexene and cyclohexane Add Br2/CCl4 or KMnO4. The cyclohexene will undergo addition and there will be a color change from orange to colorless or purple to brown,. The cyclohexane will not react. 3 6. a. For each of pair of compounds below, decide which one is more soluble in water and explain why. (8) propanol and propanone Propanol. It has both a hydrogen on an oxygen and oxygen that can hydrogen bond with water while propanone has only an oxygen N, N-diethyl ethanamide and N-ethyl butanamide N-ethyl butanamide. It has a nitrogen and a hydrogen on the nitrogen to hydrogen bond with water. The disubstituted amide does not have a hydrogen attached to a nitrogen. b. Rank the compounds below in order from lowest (1) to highest (4) boiling point and explain your ranking. (8) propanone propanol ethyl methyl ether ethanoic acid ___2______ __3______ ____1_____ ____4______ While all of these compounds contain oxygen and hydrogen, only ethanoic acid and propanol can hydrogen bond with molecules of the same compound because one hydrogen is on oxygen. Ethanoic acid has the most possible interactions. Propanone’s oxygen is more likely to induce a dipolar interaction than the ether. 7. H 3C Complete the following reactions supplying the appropriate product(s) or reactants(s). (40) H2 OH H2 H2 H + CH C C 3 CH 3 C C H2O/H H 3C C C C C H2 -----------------------> H2 CH 3 CH 3 H2 C H 3C H2 C CH OH C CH 3 No reaction O LiAlH4 -----------------------> O C C H2 Cu2+ -----------------------> OH CH 3 CH ______________________ C H2 4 CH 3 O O H2 C C O CH 3 C NaOH -----------------------> ONa+ H2 C + HO CH 3 HBr ? ---------------Br OH H H2 C C O K2Cr2O7 -------------------------> CH 3 C H2 O C H2 + H3C O O C C O H2 C C C H2 CH 3 C H2 O -----------------> CH 3 C N H NH 2 CH 2 HN CH 3 O + HCl -------------------> CH 2 -Cl+H 2N ___________________________ 5 CH 3 CH3 C HO CH 3 6. BONUS: For the alkaloid of your choice, provide the following information: (8) a. name ____________________________ b. chemical formula c. drug action 6