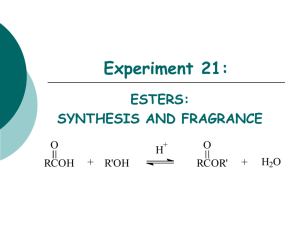
Organic Reactions Summary Sheet
advertisement

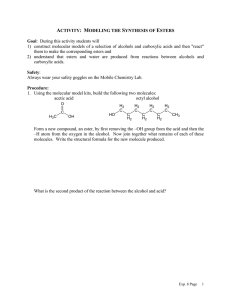
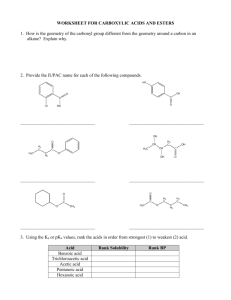
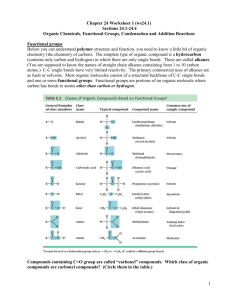
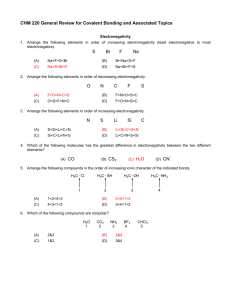
Organic Reactions Summary Sheet Reactants Alkanes + Oxygen Products Conditions Complete: CO2 and water Little bit of heat to get it going and plenty of oxygen Little bit of heat to get it going, and not enuf O2, oxygen is limiting reactant UV light, hv Incomplete: CO and water + Halogen (F2, Cl2, Br2, I2) haloalkane Classification Combustion (also redox reactions) Uses /Other Example 2 C4H10 + 13 O2 8 CO2 +10h2o 2 C4H10 + 9 O2 8 CO + 10 H2O H Substitution H H + H h Cl Cl Cl H H H methane chloromethane h CO harmful to humans, unburned hydrocarbons produce smog H Cl H h Cl Cl H Cl Cl dichloromethane Addition Dihaloalkane H H H H + chloroform H H Br2 dissolved in dichloromethane is used to distinguish between alkenes and alkanes. If reddish-brown color of Br2 disappears when added to unknown, the unknown has alkenes in it. H H + hydrogen Alkane Platinum or palladium catalyst Addition (also called reduction) H H H H PtO2/Pd + Hydrogenation of oil for margarine H H H H H tetrachloromethane also: carbontetrachloride Uses: makes starting material for PVC and Indication of akenes Cl Cl Cl Cl Cl Cl also: trichloromethane Alkenes + halogen (F2, Cl2, Br2, I2) Cl h Cl H H H + acid halide (HF, HCl, HBr, HI) + water Addition Haloalkane H H H + oxidizing agent (KMnO4 or K2Cr2O7) H H H H Alcohol Acid conditions Addition H H H Alcohols + Carboxylic acid + H Haloalkanes are useful starting materials for organic syntheses H Cl H Cl Ester + water Acidic solution and heat CH3 Condensation For incomplete oxidation: Distillation in acidic aqueous soln + O commercial manufacture of ethanol H H H H O H3C Primary: Aldehyde acid H O H H CH3 O + H3C OH OH H3C Oxidation OH propan-1-ol acid, + K2Cr2O7 O CH3 acid O H 1-propanal Esters are used in flavouring agents, plasticizers, as solvents in perfume, polyesters Primary: Carboxylic Acid Secondary: ketone For complete oxidation: Heat under reflux in acidic aqueous soln Heat under reflux in acidic aqueous soln + OH acid K2Cr2O7 O OH propanoic acid propan-1-ol OH + acid K2Cr2O7 O butan-2-ol Carboxylic acid + alcohol Ester, see above example Amide + water + amine + base (e.g. NaOH) See above Condensation difficult to conduct since amine (a base) and acid neutralize each other. Other rxns that “protect” F.G. are required Condensation See above Amide, see above example O + H3C H3C OH NH2 acid, H3C O + NaOH acid, H3C Amine + Carboxylic acid See above O Neutralization Organic salt and water butan-2-one Condensation See above Distillation Apparatus H3C CH3 O + H2O O-Na See above See above Heating under reflux condensing tube water out aldehyde vapor OH NH condensing tube water in water in boling solution To distill you heat up the solution and collect the vapor peptide bond formation, polymerization reactions to make nylons water out vapor condenses and falls back into flask condensed aldehyde out boling solution heat under reflux means you want to heat it for a long time w/o having it evaporate to heat under reflux you need to attached a condensing tube to your flask so that vapors condense before they can escape