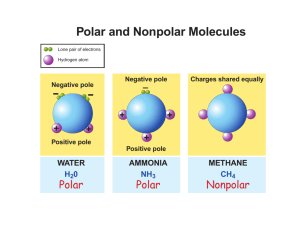
Study Guide questions for ch

Study Guide Solutions for ch. 1-3. Name __ key _____ Date _____ Pd. ____
1.
Diagram the steps of the scientific method and explain each step.
2.
Be able to use scientific notation, significant digits (pg 15 has practice probs)
3.
Convert using the metric system (practice wksts on my website)
4.
What are the SI base units for length, mass, temperature, time?
Length – meter, mass – kilogram, temperature – kelvins, time - seconds
5.
When do you use circle, line, bar graphs?
Circle when comparing parts of a whole, bar graphs when comparing multiple items that are not dependent, line graph when you are showing a dependence, causal relationship.
6.
What is different between suspensions, colloids, solutions?
Suspensions settle out, block light, can be filtered
Colloids do not settle out, have small & large particles, block light, cannot be filtered
Solutions do not settle out, have small particles, let light through, and cannot be filtered
7.
What is similar between solutions & colloids?
Neither settles out
8.
What is similar between suspensions & colloids?
Both block light
9.
What are the types of matter and are they pure substances or mixtures?
Elements & compounds are pure substances
Heterogenous & homogenous are mixtures
10.
What is the difference between a physical and chemical change?
In a chemical change the bonds in a substance break and new bonds are formed, creating a different substance. In a physical change, the physical properties may be changed, but the substance is chemically still the same.
11.
Give examples of physical and chemical changes.
Vary: Cutting hair, grass, paper – pc
Burning toast, eggs, cookies – cc
Salt & Water mixing – pc
Ice melting, water freezing or boiling – pc
Iron rusting after exposure to oxygen - cc
12.
What are some examples of physical and chemical properties?
PP – viscosity, hardness, boiling or freezing point, malleability, conductivity
CP – reactivity, flammability
13.
How could you tell the hardness of an object?
Try scratching two objects together. The one with the gouge is softer.
14.
What are two common methods to separate a mixture, and how do they separate?
Filtering – separates by size of particles
Distillation – separates by boiling points
15.
What is the difference between a mixture and a pure substance?
Pure Substances have fixed chemical compositions while mixtures do not have fixed compositions, therefore the properties may vary in samples of a mixture.
16.
What are three common types of evidence for a chemical change?
Formation of a precipitate, color change, production of a gas
17.
What is a precipitate?
When two liquids are mixed together and solid particles form, the solid formed is a precipitate.
18.
Describe or draw a diagram showing how materials can be classified as solids, liquids, gases based on whether their shapes and volumes are definite or variable.
Solids have a definite shape and volume.
Liquids have a variable shape and definite volume.
Gases have a variable shape and volume.
19.
What does the kinetic theory of matter state about particles of matter?
The kinetic theory of matter states that all particles of matter are in constant motion.
20.
What factors (3) affect the pressure of an enclosed gas?
The factors affecting the pressure of an enclosed gas are temperature, volume, and
The number of particles.
21.
If you increase temperature what happens to pressure if volume and # particles are constant?
If you increase temperature, the pressure also increases.
22.
If you decrease volume what happens to pressure if temperature and # particles are constant?
If you decrease volume, the pressure increases
23.
If you increase # particles what happens to pressure if volume and temperature are constant?
If you increase # of particles, the pressure also increases
24.
What units of temperature must be used in Charles’ Law?
The units of Kelvin must be used for temperature in Charles’ Law.
25.
In Charles Law, if you increase volume, does temperature increase or decrease?
If you increase volume, the temperature increases also.
26.
In Boyle’s Law, if you increase volume, does pressure increase or decrease?
If you increase volume, the pressure decreases.
27.
Is a phase change reversible? Is a phase change a physical or chemical change?
A phase change is reversible and it is a physical change.
28.
What happens to the temperature of a substance during a phase change? What happens to the energy during a phase change?
The temperature of a substance stays the same during a phase change. The energy of a substance changes during a phase change.
29.
Which of the phase changes are endothermic? Which are exothermic?
Melting, sublimation, vaporization, boiling, evaporation are endothermic changes.
Freezing, deposition, condensing are exothermic changes.