Colligative Properties: Notes on Solutions & Colloids
advertisement

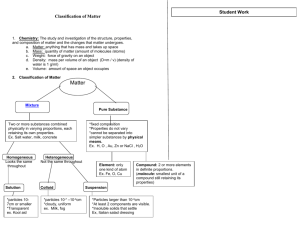
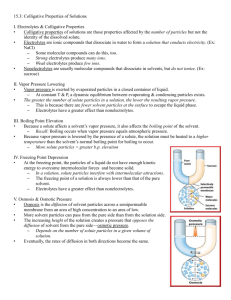
Colligative Properties Notes Colligative Properties The presence of solutes cause solution to behave differently than their pure solvent. These new properties are called colligative properties. Colligative properties depend on the amount of particles dissolved, NOT the type of particles. Vapor Pressure Depression The presence of a solute often causes the vapor pressure to drop. Thus is because the solute particles fill positions that are normally occupied by solvent molecules. Thus fewer solvent molecules escape the solution. Boiling Point Elevation The presence of solutes often raise the boiling point of the solutions. 1 mole of particles in 1 kg of water elevates the boiling point of water by 0.512 degrees C. The more concentrated a solution is, the greater the boiling point elevation will be. Freezing Point Depression. Solutions freeze at lower temperatures than their pure solvents. A 1 molal solution of sugar in water freezes at -1.86 deg. C. The more concentrated the solution, the more the freezing point will be lowered. Antifreeze Antifreeze affects both the boiling and freezing points of water. It prevents water in the radiator from freezing in the winter by lowering the freezing point and it prevents water from boiling in the summer because it also raises the boiling point of water. Osmotic Pressure Osmosis is the process in which water moves across a semi-permeable membrane. It occurs because the water molecules are trying to reach equilibrium on either side of the membrane. Osmotic pressure is the amount of pressure required to prevent osmosis from occuring. The more solute particle there are in a solution, the higher the osmotic pressure will be. Colloids Solutions are homogeneous mixtures that do not separate. Homogeneous means that the particles are evenly distributed in the solution. A supsension contains larger particles that eventually settle out of the mixture (Ex. silt). A colloid is a mixture that contains small particles dispersed in a medium. (Ex. fog) Colloids can be solid, liquid, or gas. Foams, aerosols, and gels are common colloids. Tyndall Effect Named for John Tyndall, the physicist who demonstrated that the particle in colloids were large enough to scatter light waves. A beam of light will pass through a solution without being seen. The same beam will be visible when it passes through a colloid because the particles are larger and disturb the light waves.