Zoo/Bot 3333
advertisement

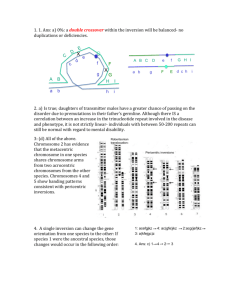
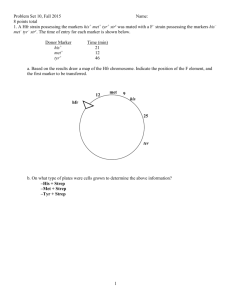
Zoo/Bot 3333 Genetics Quiz 3 10/27/06 For the answers to the quiz, please click here 1. Consider the following karyotype on the right: This individual would be expected to be which of the following. a) a normal female; b) a Turner Syndrome female with Down Syndrome; c) a female with Down Syndrome; d) a male with Down Syndrome; e) a translocation heterozygote at risk of having a Down Syndrome child. 2. Albinism in humans is an example of what type of mutation? a) morphological; b) somatic; c) nutritional; d) gain of function; e) haploinsufficient. 3. The cartoon on the right represents an ideogram of the G-Banding patterns for the human and chimpanzee chromosome sets. The human chromosomes are on the left, and the chimpanzee chromosomes are on the right. In comparing the patterns, we see evidence of which events in primates? a) a Robertsonian translocation for chromosome two; b) a pericentric inversion for chromosome 4; c) a pericentric inversion for chromosome 5; d) all of the above; e) none of the above. 4. In Drosophila, which type of chromosomal change produces a variegated position effect? a) a euchromatic deletion; b) an inversion that moves a gene from euchromatin into or near heterochromatin; c) a paracentric inversion within euchromatin that falls between genes; d) Barr body formation; e) genomic imprinting. 5. Drosophila carrying duplications of the salivary chromosome bands shown in the figure below were examined to determine the amount of a particular enzyme. The normal diploid has about 100 units of enzyme, and in the strains with duplications the enzyme amounts are: Dup 1: 143; Dup 2: 152; Dup 3: 160; Dup 4: 155; Dup 5: 148; Dup 6: 98. The region of the genome containing the gene for the enzyme can be most accurately localized to: a) Band 1: b) bands 2-7; c) Band 3-4; d) Band 3; e) Band 4. a+ b+ c+ d+ e+ 6. In the genotype shown in the figure on the right, the dashed line represents an inverted segment of the a d c b e chromosome. From this individual, rare offspring were obtained that carry a+ b+ c d+ e+. What events occurred during meiosis in the inversion heterozygote that explain these progeny? a) the chromosomes must have undergone nondisjunction; b) a single crossover occurred in the inversion loop between non-sister chromatids; c) a four strand double crossover occurred in the inversion loop; d) two crossovers occurred in the inversion loop between the same non-sister chromatids; e) two crossovers occurred outside the inversion loop between different non-sister chromatids. Questions 7 and 8 pertain to the following. Four E. coli strains of genotype a+b− are labeled 1, 2, 3, 4. Four strains of genotype a−b+ are labeled 5, 6, 7 and 8. The two genotypes are mixed in all possible combinations and (after incubation) are plated to determine the frequency of a+b+ recombinants. The results indicated in the table are obtained, where M = many recombinants, L = low numbers of recombinants, and 0 = no recombinants. The strains can be classified as 3 sex types: either F−, F+ or Hfr with regard to a and b gene transfer. strains 5 6 7 8 1 M M 0 0 2 0 0 L L 3 L L 0 0 4 M M 0 0 7. Which of the following can be classified as F - cells? a) 1, 2, 4; b) 5, 6, 8; c) 2, 5, 6; d) 7, 3; e) none of the above. 8. True or false. Suppose after mixing strains 2 and 7 the culture was left to grow on medium containing the nutrients needed by the a- and b- mutants. Virtually all of the progenitor cells arising from the mixture would be expected to have pili if examined under the electron microscope. Five interrupted-mating experiments are performed with E. coli. Five different x y strs Hfr strains are mixed in separate experiments with an x y F strr strain. The progeny are screened on appropriate selective media to detect recombinants. The number of minutes after the start of the experiment that the x and y genes are first detected in the recombinants (i.e their time of entry) is given in the chart below. In the figure below, the whole chromosome has been divided into a 100 minute map; each mark on the circle represents 5 minutes. For orientation, the origin of replication for HfrA is located at “12 o’clock” on the map, and the genes for Hfr A will be donated in a clockwise direction (i.e. following the arrowhead). Cross Hfr A x F Hfr B x F Hfr C x F Hfr D x F Hfr E x F Entry time (in minutes) for Hfr wild type genes x+ gene y+ gene 15 75 45 5 65 5 10 50 65 25 9. The integration site for Hfr B is how many minutes away from the integration site for Hfr A? a) 5 minutes; b) 15 minutes; c) 20 minutes; d) 30 minutes; e) 45 minutes. 10. True or false. The integration sites for Hfr A and Hfr B both lead to genes being donated in the same relative orientation (same direction).