Lecture 24 – Bacterial genetics I. Prokaryotes – an overview A
advertisement
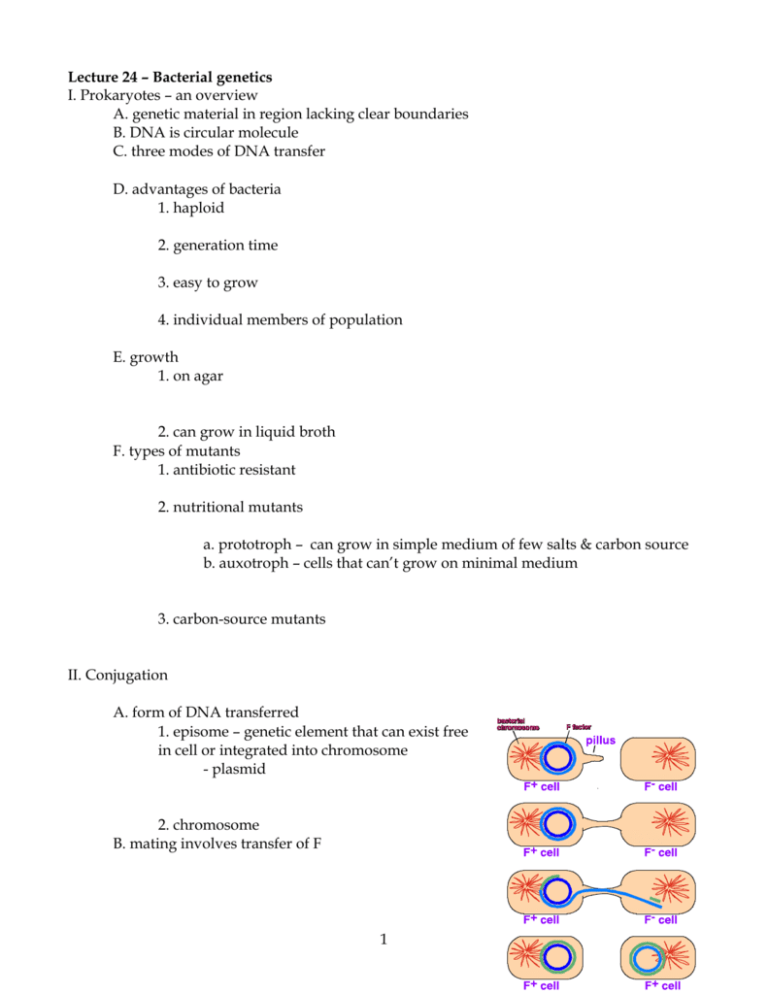
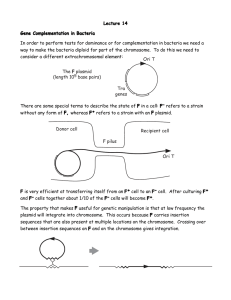
Lecture 24 – Bacterial genetics I. Prokaryotes – an overview A. genetic material in region lacking clear boundaries B. DNA is circular molecule C. three modes of DNA transfer D. advantages of bacteria 1. haploid 2. generation time 3. easy to grow 4. individual members of population E. growth 1. on agar 2. can grow in liquid broth F. types of mutants 1. antibiotic resistant 2. nutritional mutants a. prototroph – can grow in simple medium of few salts & carbon source b. auxotroph – cells that can’t grow on minimal medium 3. carbon-source mutants II. Conjugation A. form of DNA transferred 1. episome – genetic element that can exist free in cell or integrated into chromosome - plasmid 2. chromosome B. mating involves transfer of F 1 - conjugation schematic C. Hfr - high frequency of recombination D. Hfr mating: E. a few points 1. 100 minutes to transfer entire chromosome 2. mating pair usually separates before entire chromosome transferred 3. recipient remains F- because part of F not transferred 4. incorporated region replaces endogeneous region of chromosome 5. need to be able to identify recombinants to map genes F. time of entry mapping (uses Hfr and F- strains) 1. transfer begins at one point, proceeds in one direction 2. longer the mating, the more donor chromosome transferred 2 3. can map genes by time of entry a. b. c. d. example: cross is: Hfr a+ b+ c+ d+ X F- a- b- c- d- str-r 1. # recombinants increases with time 2. for each, is a time before which no recombinants 3. intercept with x-axis is time of entry 4. # recombinants reaches max, which decreases as TOE increases G. F’ plasmid 1. F may excise from Hfr 2. sometimes excision imprecise, plasmid includes chromosomal sequences this is F’ 3. produce cells diploid for region of chromosome merodiploid – 4. permit tests of dominance and effects of gene dosage 3 IV. Transformation – take up of free DNA from environment A. many bacteria capable of this - may be in form of plasmid - plasmid B. Particular problem in spread of drug resistance between strains 4