Quiz 3
advertisement
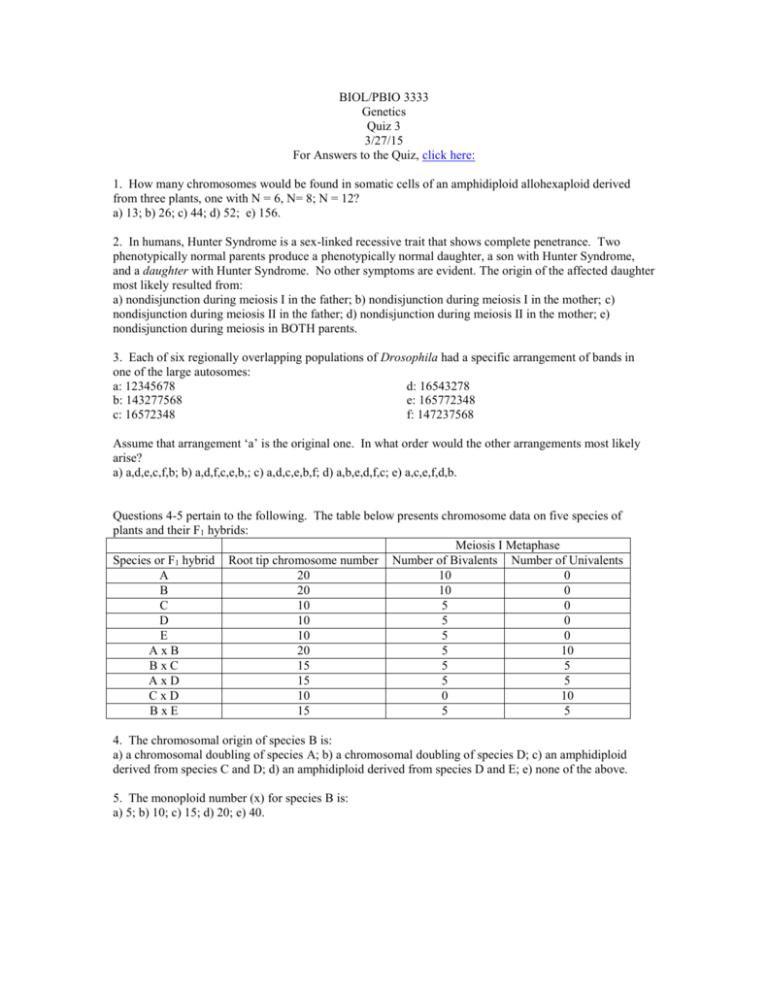
BIOL/PBIO 3333 Genetics Quiz 3 3/27/15 For Answers to the Quiz, click here: 1. How many chromosomes would be found in somatic cells of an amphidiploid allohexaploid derived from three plants, one with N = 6, N= 8; N = 12? a) 13; b) 26; c) 44; d) 52; e) 156. 2. In humans, Hunter Syndrome is a sex-linked recessive trait that shows complete penetrance. Two phenotypically normal parents produce a phenotypically normal daughter, a son with Hunter Syndrome, and a daughter with Hunter Syndrome. No other symptoms are evident. The origin of the affected daughter most likely resulted from: a) nondisjunction during meiosis I in the father; b) nondisjunction during meiosis I in the mother; c) nondisjunction during meiosis II in the father; d) nondisjunction during meiosis II in the mother; e) nondisjunction during meiosis in BOTH parents. 3. Each of six regionally overlapping populations of Drosophila had a specific arrangement of bands in one of the large autosomes: a: 12345678 d: 16543278 b: 143277568 e: 165772348 c: 16572348 f: 147237568 Assume that arrangement ‘a’ is the original one. In what order would the other arrangements most likely arise? a) a,d,e,c,f,b; b) a,d,f,c,e,b,; c) a,d,c,e,b,f; d) a,b,e,d,f,c; e) a,c,e,f,d,b. Questions 4-5 pertain to the following. The table below presents chromosome data on five species of plants and their F1 hybrids: Meiosis I Metaphase Species or F1 hybrid Root tip chromosome number Number of Bivalents Number of Univalents A 20 10 0 B 20 10 0 C 10 5 0 D 10 5 0 E 10 5 0 AxB 20 5 10 BxC 15 5 5 AxD 15 5 5 CxD 10 0 10 BxE 15 5 5 4. The chromosomal origin of species B is: a) a chromosomal doubling of species A; b) a chromosomal doubling of species D; c) an amphidiploid derived from species C and D; d) an amphidiploid derived from species D and E; e) none of the above. 5. The monoploid number (x) for species B is: a) 5; b) 10; c) 15; d) 20; e) 40. 6. Deletions can be used to determine the orientation of genes on a chromosome. A series of 6 overlapping deletions "uncovered" the following recessive mutations in deletion heterozygotes, allowing them to show a recessive phenotype in the heterozygotes (i.e. ‘pseudodominance’): deletion 1: r, s deletion 4: deletion 2: k, r, s deletion 5: deletion 3: o, p, z deletion 6: The order of the genes can be represented: a) krsopzn; b) nozsrpk; c) rskzopn; d) kropsnz; e) npzorsk. o, z z, k, s n, p 7. Which of the following are true? a) mutations causing a change in phenotype occur rarely; b) different genes mutate at different rates; c) disruption of gene function through mutation occurs at higher frequency than restoration of function through mutation; d) all of the above; e) none of the above. Questions 8 and 9 pertain to the following. Four E. coli strains of genotype a+b− are labeled 1, 2, 3, 4. Four strains of genotype a−b+ are labeled 5, 6, 7 and 8. The two genotypes are mixed in all possible combinations and (after incubation) are plated to determine the frequency of a+b+ recombinants. The results indicated in the table are obtained, where M = many recombinants, L = low numbers of recombinants, and 0 = no recombinants. The strains can be classified as 3 types relative to conjugation: either F−, F+ or Hfr with regard to a and b gene transfer. strains 5 6 7 8 1 L 0 L 0 2 0 L 0 M 3 M 0 M 0 4 L 0 L 0 8. Which of the following can be classified as F - cells? a) 2, 5, 7; b) 2, 3, 6; c) 1, 4, 6; d) 3, 8; e) none of the above. 9. True or false. Suppose after mixing strains 2 and 8 the culture was left to grow on medium missing the nutrients needed by the a- and b- mutants. Virtually all of the cells arising from the minimal media plate would be expected to have pili if examined under the electron microscope. Five interrupted-mating experiments are performed with E. coli. Five different x+y+ z+ strs Hfr strains are mixed in separate experiments with an x−y−z−F− strr strain. The progeny are screened on appropriate selective media to detect recombinants. The number of minutes after the start of the experiment that the x, y and z genes are first detected in the recombinants (i.e their time of entry) is given in the chart below; if the gene has not been transferred, it is indicated as nt (no transfer). In the figure below, the whole chromosome has been divided into a 100 minute map; each mark on the circle represents 5 minutes. For orientation, the origin of replication for HfrA is located at “12 o’clock” on the map, and the genes for Hfr A will be donated in a clockwise direction (i.e. following the arrowhead). Cross Hfr A x F Hfr B x F Hfr C x F Hfr D x F Hfr E x F Entry time (in minutes) for Hfr wild type genes x+ gene y+ gene 15 45 z+ gene nt 5 65 nt 35 50 10 nt 5 30 50 nt 5 10. The integration site for Hfr D is how many minutes away from the integration site for Hfr E? a) 5 minutes; b) 10 minutes; c) 25 minutes; d) 30 minutes; e) 45 minutes.