Lecture 12
advertisement

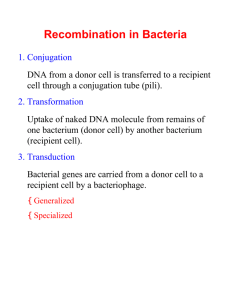
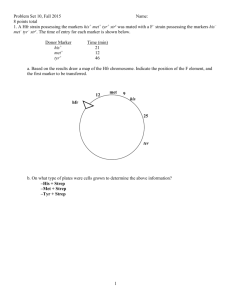
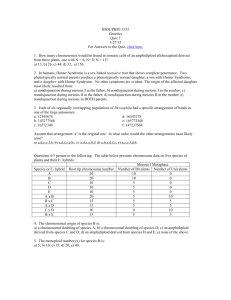
Overview of Conjugation F+ x F- F+, F+ products Generation and transfer of Hfr chromosome Insertion of the F factor into the E. coli chromosome • Multiple positions • Two orientations The order of gene transfer depends the position and the orientation of the inserted F facter in the Hfr chromosome Transfer of the integrated F factor results in transfer of genomic markers Hfr a+ x F- a- Hfr a+ + F- a+ Two types of conjugation. F+ x F- crosses 107 F+ cells x 107 F- cells 104 different Hfrs All markers transferred equally at about 1/107 frequency Hfr x F- crosses 107 Hfr cells x 107 F- cells all 107 same Hfr Markers transferred in specific order at about 1/104-1/103 frequency Hfr Strain1 = MZXWC 2 = LANCW 3 = ALBRU 4 = ZMURB MZXWC WCNAL ALBRU BRUMZ M Z U R X B W L C A N The Genetic Map of Ecoli minutes How to do fine scale mapping. Interrupted mating experiments cannot distinguish the relative position of genes within about 2 minutes of each other, and thus give only a rough idea of gene location. Do 1. Three point crosses. 2. Reciprocal crosses. Both use recombination frequencies to determine gene order. Lets look more closely at what happens in the Fcell (the exconjugant). Recombination (crossover) in F- cell. incomplete genome from the donor Hfr chromosome. complete genome from F- cells Interrupted mating says: mal arg/met 10 minutes 6 minutes Use a 3 point cross to figure out order of arg and met. Hfr strsarg+met+mal+ X F- strRarg-met-mal- How to do the experiment???? StrS (book says mal+,met+) StrR 1. Select for mal+, the last marker, ensures that all genes transfer. That way you only look at recombination. 2. Replica plate onto both arginine or methionine minus plates.. metarg mal Crossovers? 2 Most frequent 2 Pretty frequent 2 Less frequent, smaller interval least frequent 4 Reciprocal Crosses Another way for ordering markers that are close to one another, also takes advantage of the lower frequency of quadruple crossovers. a bc ? a cb ? or Cross I Hfr strs a+ b+ c- x F- strr a- b- c+ select strr a+ b+ c+ Cross II Hfr strs a+ b- c+ x F- strr a- b+ c- select strr a+ b+ c+ • If the order is abc, then will get many more a+b+c+ exconjugants from cross I than cross II. • If the order is acb, then will get many more a+b+c+ exconjugants from cross II than cross I. Cross 2 Cross 1 a+ b+ c- a+ b- c+ a- b+ c- a+ c+ b- Hfr Hfr If abc a- b- c+ a+ c- b+ F- Hfr Hfr If acb a- c+ b- F- Therefore If abc cross I > cross II, F- a- c- b+ If acb cross II > cross I. F- F’ elements (F prime elements) • F factors which carry a part of the chromosome. • Allows very high frequency transfer of F’ markers. • Allows one to make partial diploids. • Can use for complementation tests. Bacteria tend to cluster genes of similar function. F’ plasmids have every thing they need to transfer. Bacterial chromosome Bacterial chromosome F+ F’ metA metB metC metA metB metC Hfr F’ Bacterial chromosome Bacterial chromosome F’ F’ male metA metB metC X F- female metA metB metC Bacterial chromosome F’ metA metB metC F’ partially diploid male metA metB metC Complementation test, an example. Bacterial chromosome F’ metA- metB+ metC+ F’ met- m1 male Your met- mutant Bacterial chromosome X metA metB met??- metC F- met- m2 female Your friends met- mutant F’ metA- metB+ metC+ Bacterial chromosome metA metB met??- metC F’ partial diploid Test for complementation by growing on met- plates. If it grows on met- plates = If no growth = Different genes = complement. Same gene = fail to complement = metA-. Lederberg and Zinder, 1951 • Question: Is there conjugation in Salmonella (closely related bacteria)? – phe+trp+met-his- x phe-trp-met+his+ – Found prototrophs • Experiment: U-tube to separate two auxotrophic strains, then check for growth on minimal media U- tube experiment (phe+trp+met-his-) minimal media no prototrophs (phe-trp-met+his+) << the size of bacteria ~ the size of P22 Phage minimal media Prototrophs!! Bacterial Phage Conclusion: Instead of conjugation, they discovered phagemediated transfer of bacterial genes, or TRANSDUCTION.