x genomes
advertisement

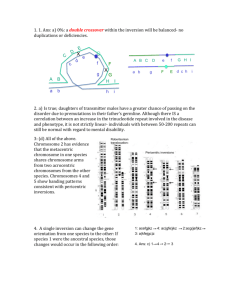
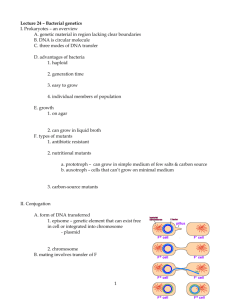
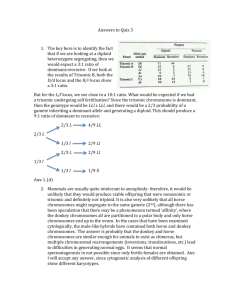
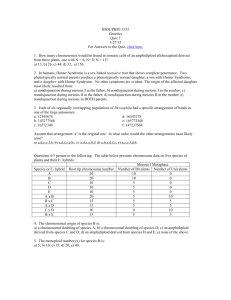
1. The cross A x B indicates that the two genomes contain different (i.e. nonhomologous chromosome sets- they do not pair (20 univalents). The A x C and A x D crosses show that each species has a chromosome set (x = 5) that pair with A (bivalent), and one set that does not pair. C x D also shows that the 5 chromosomes are not homologous. Therefore, A must have a chromosome set derived from both C and D. Since A has twice the number of chromosomes as C and D and these chromosomes have pairing partners in A, then A must be a tetraploid amphidiploid, derived from the C and D genomes. Ans: (c) 2. The monoploid number, or the number of chromosomes in a single set for species C and D is 5. Species A is a tetraploid and contains 4 sets of 5 chromosomes. Ans: (a) 3. Hunter Syndrome is an X-linked recessive, for a female to inherit it, it must be present in two copies. Therefore, the carrier mother must have undergone a non-disjunction event during Meiosis II, and passed both copies of the mutant X chromosome to a gamete. In addition, the daughter’s karyotype is not indicated. The daughter may be triplo-X, where the paternal allele is X-inactivated; this is probably most likely. It is also possible, but more unlikely, that nondisjunction occurred in both parents, and that the daughter was fertilized by a sperm containing no sex chromosome. Ans: (d), but I will accept (e). 4. If (a) is the original sequence: 12345678; Then an inversion would give the sequence (c) 15432678; A duplication of 2 would yield (f) 154322678; A deletion of 5 would yield (d) 14322678; An inversion would yield (e) 16223478. And another inversion would yield (b) 12263478. Ans: a,c,f,d,e,b. (c). 5. Amphidiploid allohexaploid: 6 chromsome sets that have been doubled. Three sets: 8 + 4 + 10 (number donated in gametes). 22 x 2 = 44. Ans: (c) 6. z+ x y z Pseudodominance: phenotype of deletion heterozygote is mutant (-) for x and y; wild type (+) for z Each deletion “uncovers” several mutations, indicating that they must be located in the same region of the genome. By comparing overlapping deletions and the mutations they uncover, a map can be constructed. It is easiest to start with the smallest deletions first and build from them. r,s k,r,s prs o,z n,z prsk p,r zoprsk nzoprsk o,p,z Ans: (e) 7. See your textbook, chapter 7 (193-94; ) All of the above are true. Ans: (d). 8. • • An F- cell would be one that could form – 1) low numbers of colonies (when conjugated with F+) – 2) many colonies (when conjugated with Hfr) – 3) no colonies (when conjugated with F-) Additionally, donor cells can only conjugate with F- cells... strains 5 F+ 6 F+ 7 F8 Hfr 1 FL L 0 M 2 F+ 0 0 L 0 3 Hfr 0 0 M 0 4 FL L 0 M 9. • • Mixing strains 1-8 is a cross between an Hfr and a F- cell. An Hfr cell will transfer certain genes at high frequency, but the conjugation bridge will usually break before all of the F factor is transferred. Thus, ex-conjugants can’t be donors. Ans: false. 10. Cross Hfr A x F Hfr B x F Hfr C x F Hfr D x F Hfr E x F Entry time (in minutes) for Hfr wild type genes x+ gene y+ gene 35 55 30 10 5 25 65 45 40 20 The x and y genes are located 30 minutes and 55 minutes from the intergration site for A. This allows us to identify unambiguously the integration sites for the other Hfrs: D E C x y B 10. Doing this, we find B is integrated 10 minutes away from E. Ans: (b) 11. A is being donated in a clockwise direction; B is being donated in a counter clockwise direction. Ans: false