Problem Set 6
advertisement

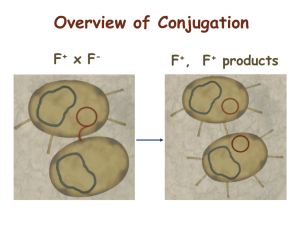
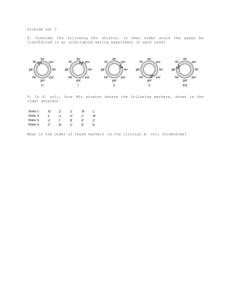
Problem Set 10, Fall 2015 Name: 8 points total 1. A Hfr strain possessing the markers his+ met+ tyr+ strs was mated with a F– strain possessing the markers his– met– tyr– strr. The time of entry for each marker is shown below. Donor Marker his+ met+ tyr+ Time (min) 21 12 46 a. Based on the results draw a map of the Hfr chromosome. Indicate the position of the F element, and the first marker to be transferred. 12 met 9 his hfr 25 tyr b. On what type of plates were cells grown to determine the above information? –His + Strep –Met + Strep –Tyr + Strep 1 Problem Set 10, Fall 2015 Name: 8 points total 2. In three different interrupted mating experiments, you obtain the following data for the time of entry of the following genes: arg, met, leu, ser, gal, val, and phe. All of these experiments were conducted using Hfr strains (Hfr 1, Hfr 2, and Hfr3) derived from the same original strain of E. coli. Experiment 1 (Hfr 1) Met 10 min Val 25 min Leu 30 min Arg 40 min Ser 55 min Gal 60 min Experiment 2 (Hfr 2) Experiment 3 (Hfr 3) Gal 5 min Leu 5 min Ser 10 min Val 10 min Leu 35 min Met 25 min Val 40 min Phe 55 min Met 55 min Gal 75 min Phe 85 min Ser 80 min a. Determine the order of these genes on the bacterial chromosome and draw a single map showing the position of each of these genes on the bacterial chromosome. Based on the time intervals above, indicate the map distances between each gene, expressed in minutes. Also show the origin of transfer and direction of transfer for each Hfr. hfr1 10 met 15 val 5 leu 5 hfr3 5 arg 20 15 ser phe 5 15 5 gal hfr2 b. If the crosses were set up as described in class, what are the genotypes of the donor and recipient cells? Donor: Hfr arg+ ser+ gal+ phe+ met+ val+ leu+ strpS Recipient: F- arg- ser- gal- phe- met- val-1 leu- StrpR 2 Problem Set 10, Fall 2015 Name: 8 points total 3. In three different interrupted mating experiments, you obtain the data shown below for the time of entry. All experiments use Hfr strains derived from the same original parent strain. Hfr1 miy 10 min sow 20 min raj 35 min nub 40 min tod 50 min mic 65 min sha 75 min Hfr2 sow 5 min miy 15 min chr 30 min sha 40 min mic 50 min tod 65 min nub 75 min Hfr3 mic 5 min tod 20 min nub 30 min raj 35 min sow 50 min miy 60 min chr 75 min a. Show the genetic map for each of these genes on the circular chromosome. Indicate the location of each origin and the direction of transfer. Doesn’t need to be drawn to scale. hfr1 5 chr 10 sha 5 hfr3 5 mic 10 15 miy tod 10 10 sow nub 5 5 10 raj hfr2 b. What are the genotype of the donor and recipient strains? Hfr miy+ sow+ raj+ nub+ tod+ mic+ sha+ chr+ StrS F– miy- sow- raj- nub- tod- mic- sha- chr- StrR 3 Problem Set 10, Fall 2015 Name: 8 points total 4. The exotic tropical tree frog E. qinae normally has 13 pairs of chromsomes (i.e. 2n = 26). You find a number of unusual individuals with the chromosome content shown below. Please fill in the blanks for each of the variants in the table below: # chromosomes ploidy of individual 25 monosomy 13 monoploid 28 could be double trisomy or tetrasomy 52 tetraploid 27 trisomic 5. In an interrupted mating mapping experiment, you obtain the results shown in the graph below. The experiment was conducted as described in class. a. Show the genetic map for each of these genes on the circular chromosome. Indicate the location of the origin and the direction of transfer. Doesn’t need to be drawn to scale. hfr trp 3 4 met 7 leu 7 arg 5 lys b. What are the genotypes of the donor and recipient strains? donor: Hfr trp+ met+ leu+ arg+ lys+ StrS recipient: F- trp- met- leu- arg- lys- StrR c. For each gene, the number of recombinants increases with time until they reach a maximum. Why does the number of recombinants for a given gene increase with time? The matings to not all begin at the same time. d. Why does the number of recombinants reach a maximum? The probability of separation is balanced by the probability of new matings. 4 Problem Set 10, Fall 2015 Name: 8 points total 6. Compare and contrast the three modes of bacterial DNA transfer. Conjugation – involves direct cell-cell contact through a cytoplasmic bridge. Involves transfer of fertility factor (F+), part of bacterial chromosomes (Hfr) or F’ transformation – involves take up of free DNA from the environment, no direct cell-cell contact transduction – transfer of DNA between bacteria by virus, no direct cell-cell contact 7. In a transduction mapping experiment, you get the following results. experiment 1 2 selected marker a+ b+ unselected markers 15% b+, 30% c+ 30% c+, 15% a+ a. Draw the relative position of a, b and c. a c b b. a, b and c are enzymes required for the synthesis of A, B and C, respectively. An a mutant can’t grow without A in the media, etc. How are the above recombinants identified? In experiment 1, cells were plated on plates that lacked A and then replica plated to places that lacked B and plates that lacked C. In experiment 2, cells were plated on plates that lacked B and then replica plated to plates that lacked A and plates that lacked C. 8. In studying a particular animal, you find that the fourth chromosome is unusual. The two copies of chromosome 4 are shown. The normal chromosome is shown on the top, and the unusual one is shown on the bottom. The position of seven genes is shown. a. What is the specific name of the chromosomal alteration that generated the abnormal chromosome? pericentric inversion b. Show the two chromosomes synapsed in meiosis. Please include the genes. too hard to draw in the computer, it involves formation of an inversion loop to bring homology together. c. What effect will the rearrangement in the unusual chromosome have on recombination? Why? It will appear to suppress recombination because gametes produced by crossing over in the inverted region will be inviable. d. You find an individual homozygous for the abnormal chromosome (i.e. the bottom chromosome). Show it’s chromosomes synapsed in meiosis. Please include the genes. 5