naming molecular compounds
advertisement
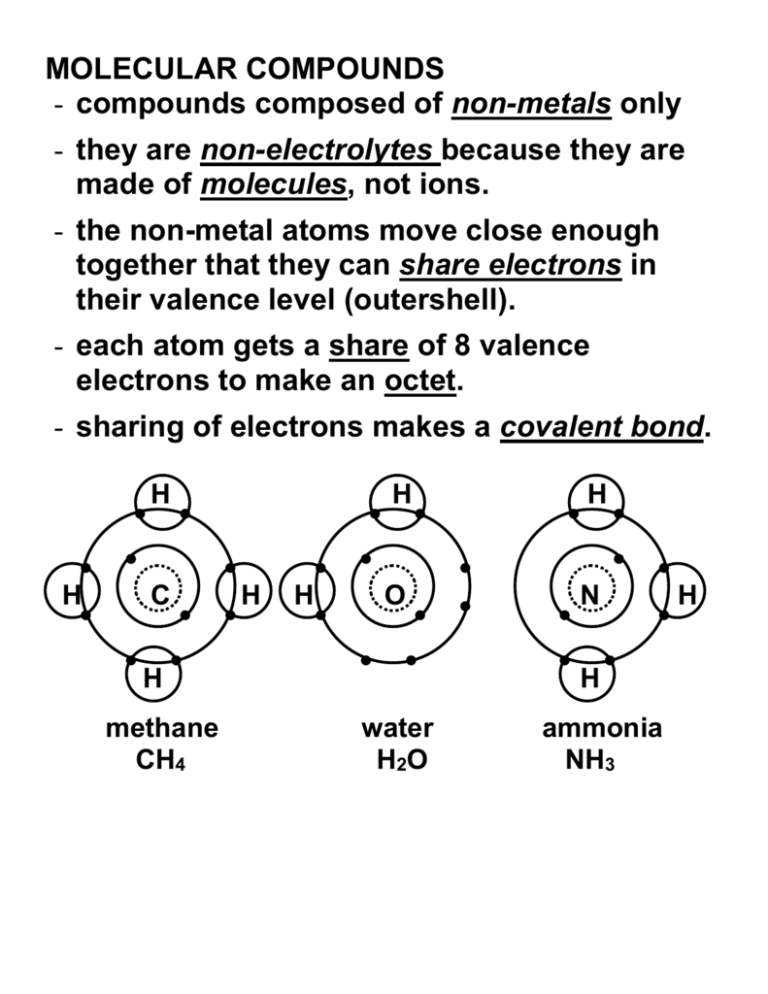
MOLECULAR COMPOUNDS - compounds composed of non-metals only - they are non-electrolytes because they are made of molecules, not ions. - the non-metal atoms move close enough together that they can share electrons in their valence level (outershell). - each atom gets a share of 8 valence electrons to make an octet. - sharing of electrons makes a covalent bond. H H C H H H H O N H methane CH4 H water H2O ammonia NH3 H TO PREDICT FORMULAS OF MOLECULAR COMPOUNDS: Follow the same rules as ionic compounds. Example: carbon combining with oxygen STEP 1: Write element symbols and valence STEP 2: Make the number of positives equal to the number of negatives STEP 3: Reduce the subscript to lowest terms, omit any subscript of 1 CO2 is carbon dioxide - the carbon shares 4 electrons, each oxygen shares 2 of their electrons O C O double bonds (2 pairs of electrons each) Non-metal atoms may combine in different ways with each other. This results in molecular formulas that we wouldn’t normally predict. Ex. CO Carbon monoxide - the carbon shares 2 of its electrons, the oxygen shares 4 of its electrons O C triple bond (3 pairs of electrons) NAMING MOLECULAR COMPOUNDS Some molecular compounds have common names: H2O NH4 CH4 But there is a proper names for all molecular compounds. The method is similar to that for ionic compounds. However, when the formula contains more than one atom of a non-metal, we add a prefix indicate the number of atoms. The ending of the second non-metal is changed to “ide”. The prefixes used are: number prefix number 1 mono 6 2 di 7 3 tri 8 4 tetra 9 5 penta 10 prefix hexa hepta octa nona deca Note: The prefix “mono” is omitted at the beginning of all compound names, except for Carbon Monoxide. Examples: H2O NH4 CH4 Try these: i) PCl5 ii) SF2 iii) N2O5 WRITING FORMULAS FOR MOLECULAR COMPOUNDS Ex. Sulfur trioxide STEP 1: Write the symbols for each element in the same order as in the name STEP 2: Add subscripts to any symbol who’s name has a prefix. DO NOT REDUCE TO LOWEST TERMS. Try these: i) carbon disulfide ii) carbon tetrachloride iii) sulfur difluoride iv) dihydrogen monosulfide v) hydrogen monosulfide DIATOMIC MOLECULES - molecules that exist as two atoms bonded together. Many non-metal atoms exist as diatomic molecules instead of single atoms (Noble gases are all monatomic) The molecule is still named using the element’s normal name. Prefixes are not used. ALL HALOGENS ARE DIATOMIC MOLECULES F2 – fluorine Br2 – bromine Cl2 – chlorine I2 - iodine ALL GASES AT ROOM TEMPERATURE (OTHER THAN THE NOBLE GASES) ARE DIATOMIC. H2 – hydrogen O2 – oxygen N2 – nitrogen