4 - Molecular Compounds
advertisement

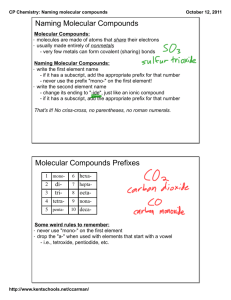
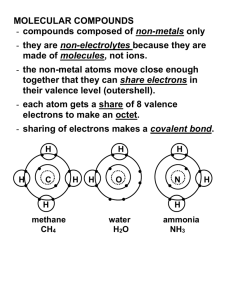
Molecular Compounds A molecular compound consists of two non-metals. They are also called covalent compounds. Recall: Ionic compounds are formed when a metal combines with a non-metal by the transfer of electrons One ion is positive, and the other is negative – therefore they attract and form an ionic bond In molecular compounds: electrons are shared between elements, NOT transferred covalent bonds are formed Example: H2 – hydrogen gas H2O – water Other examples of molecular compounds include: O2 – oxygen gas NH3 – ammonia CH4 – methane gas C12H22O11 – table sugar H2O - water C8H18 – octane Diatomic Molecules: Molecules consisting of two atoms joined by a covalent bond Atoms such as oxygen can’t exist alone – will form diatomic molecules there are seven diatomic molecules: H2 N2 O2 F2 Cl2 Br2 I2 Naming Molecular Compounds: The name of each element begins with a prefix which indicates the number of atoms of the element. Naming formula: Element 1: prefix + element name Element 2: prefix + element stem + -ide Remember: These rules only apply to two non-metals! Number Prefix Example Name 1* mono-* CO carbon monoxide 2 di- CS2 carbon disulphide 3 tri- SO3 sulfur trioxide 4 tetra- CF4 carbon tetrafluoride 5 penta- PBr5 phosphorus pentabromide 6 hexa- SF6 sulfur hexafluoride 7 hepta- 8 octa- 9 nona- 10 deca- *Note: mono- is usually omitted from the name of the first element Examples: N2O3 – _________________________________________ CCl4 – __________________________________________ trinitrogen pentoxide – _____________ silicon dioxide – _____________