CHAPTER 17 READING GUIDE
advertisement

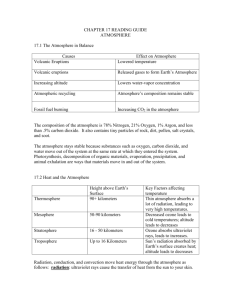
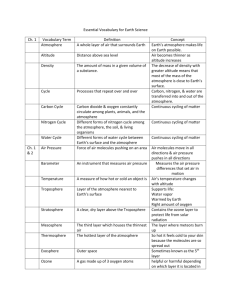
CHAPTER 17 READING GUIDE ATMOSPHERE 17.1 The Atmosphere in Balance Causes Effect on Atmosphere Volcanic Eruptions Volcanic eruptions Increasing altitude Atmospheric recycling Fossil fuel burning Key Ideas: The composition of Earth’s atmosphere remains fairly constant. Gases move continually between the atmosphere and other parts of Earth’s system. The recycling of atmospheric materials maintains a delicate balance and local events may have global consequences. The composition of the atmosphere is 78% Nitrogen, 21% Oxygen, 1% Argon, and less than .5% carbon dioxide. It also contains tiny particles of rock, dirt, pollen, salt crystals, and soot. The atmosphere stays stable because substances such as oxygen, carbon dioxide, and water move out of the system at the same rate at which they entered the system. Photosynthesis, decomposition of organic materials, evaporation, precipitation, and animal exhalation are ways that materials move in and out of the system. 17.2 Heat and the Atmosphere Vocabulary: Radiation: Conduction: Convection: Ozone: Insolation: Key Idea: Energy from the sun heats the atmosphere and Earth’s surface. This heat spreads throughout the atmosphere and is also radiated back into space. Height above Earth’s Surface Thermosphere Mesophere Stratosphere Troposphere Key Factors affecting temperature Thin atmosphere absorbs a lot of radiation, leading to very high temperatures. Decreased ozone leads to cold temperatures; altitude leads to decreases Ozone absorbs ultraviolet rays, leads to increases. Sun’s radiation absorbed by Earth’s surface creates heat; altitude leads to decreases Radiation, conduction, and convection move heat energy through the atmosphere as follows: _________________: ultraviolet rays cause the transfer of heat from the sun to your skin. ________________________: a fire’s warmth spreading to your body comes from conduction of heat from the fire to the air and then from the air to your body _______________________: when a building’s upper floors are hotter than the lower ones, convection had made the hot air raise and cool air fall. When Earth’s ___________ ___________ is balanced, its temperature remains relatively constant. If the budget becomes ______________________, Earth’s average temperatures would rise or fall depending on the direction of the imbalance. The _________________________________ captures solar radiation that would otherwise disperse back into space. 17.3 Local Temperature Variations: Many factors affect how much solar energy is absorbed by Earth’s surface at any given time and place. Vocabulary: Isotherm: 1. Factors Affecting Temperature at Given Location Intensity of Insolation Type of Surface 1. 2. 2. 3. 4. How the factors affect the temperature in a given location: Time of Day: affects the angle of the sun’s rays, with the most _________ ____________________________________________________________ Latitude: affects the angle of the sun’s rays by placing some parts of ______________________________________ than others. Time of Year: affects ____________________________________, again affecting the angle of the sun’s rays. Cloud cover reflects insolation back into space, decreasing the temperature on Earth. Land: ______________________________________________, which allows for high temps during the day and cooler temps at night, as well as temp fluctuations from day to day. Water: _________________________________________________. Water temperature does not vary at a fast rate of time. 17.4 Human Impact on the Atmosphere Vocabulary: Air pollution: Temperature inversion: Acid Rain 1. Air Pollution Global Warming Smog 1. 1. Ozone Depletion 1. 2. 2. 2. 2. 3. 3.