Air Pressure Vocabulary and Notes
advertisement

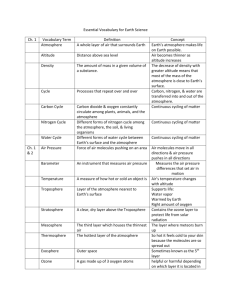
Name: _________________________ Air Pressure Vocabulary and Notes Science/Key/Block # ________ Date: _________ Air Pressure: using page 499-500 in your text, answer the following questions. 1. What is air pressure? __________________________________________________________________ 2. What concept is like air pressure? ________________________________________________________ 3. The part of the atmosphere that has the greatest air pressure is ________________________________ 4. As temperature goes _____ the pressure increases.(______pressure). 5. As temperature goes _____ the pressure decreases.(_______ pressure). 6. In ___________ __ weather there is High Pressure. 7. In _____________ weather there is Low Pressure. 8. Use the boxes to the right to show what air molecules look like under low pressure and high pressure. Low Pressure Draw six examples of air pressure in everyday life and label each drawing: High Pressure Name: _________________________ Atmosphere Vocabulary Practice Science/Key/Block # ________ Date: _________ Directions: Use vocabulary words to fill in the blanks. *Not all the words will be used!! 1. The layer of air that surrounds the Earth (like a blanket). The atmosphere is made up of a mixture of gaseous elements and compounds and a small amount of tiny solids and liquids. The atmosphere is held close to Earth due to gravity. ______________________ 2. A layer of a special kind of oxygen (ozone = O3) found in the stratosphere that protects life on Earth from the sun’s harmful ultraviolet rays.________________________ 3. “Rivers” of high-speed air in the atmosphere, found in the stratosphere. It affects air masses and affects aircraft by speeding or slowing their path._____________________ 4. The movement of air from a region of high pressure to low pressure. ____________________ 5. The outermost atmospheric layer that merges with space and contains very few molecules.________________________ 6. The middle layer of Earth’s atmosphere where most meteoroids burn up. The temperature decreases as altitude increases.___________ 7. The height above a specific point, as the surface of Earth or sea level._________________________ 8. The atmospheric layer between the mesosphere and the exosphere where the molecules contain the most heat energy; the Northern and Southern lights, known as the auroras are found here. The ionosphere. The temperature increases as altitude increases.____________ 9. The second layer from the Earth’s surface. It contains the ozone layer. The temperature increases as altitude increases due to the ozone layer’s absorption of ultraviolet rays from the sun._________________ 10. The average amount of energy from the motion of the molecules of a substance._______________________ 11. When warm air enters a region the molecules move further apart and rise usually bringing clouds and precipitation. ________________________________ 12. The transfer of heat energy by the movement of molecules from one place to another through a liquid or gas. Hot air or liquids rise because they become less dense while cold air/liquids sink due because they become denser. The fluids move in a circular pattern, or convection current as a result.___________________________ 13. The lowest layer of the atmospheric, containing about 75% of all the air in the atmosphere. It contains the air we breathe and is where weather, clouds, and air pollution are found.________ The temperature decreases as altitude increases.___________ 14. The upper parts of the atmosphere where ions (charged atoms) are found. Radio waves bounce off the ionosphere.__________ 15. A form of energy given off by light with wavelengths that is shorter than visible light. Ultraviolet rays are harmful to living things._________________ 16. The transfer of energy (including heat) through electromagnetic (light) waves. Examples include: radio, microwave, infrared, ultraviolet, visible light, x-rays, gamma rays ________________________ 17. When heat is transferred between solid substances by direct contact. _______________________