Essential Vocabulary for Earth Science Ch. 1 Vocabulary Term
advertisement
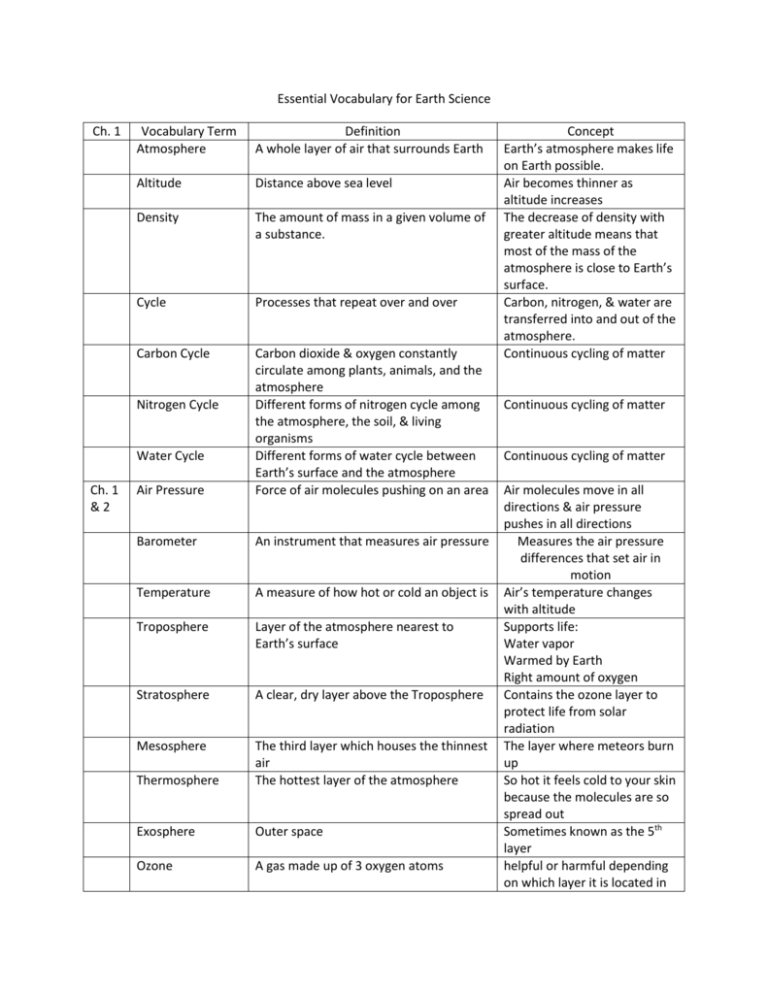
Essential Vocabulary for Earth Science Ch. 1 Vocabulary Term Atmosphere Definition A whole layer of air that surrounds Earth Altitude Distance above sea level Density The amount of mass in a given volume of a substance. Cycle Processes that repeat over and over Carbon Cycle Air Pressure Carbon dioxide & oxygen constantly circulate among plants, animals, and the atmosphere Different forms of nitrogen cycle among the atmosphere, the soil, & living organisms Different forms of water cycle between Earth’s surface and the atmosphere Force of air molecules pushing on an area Barometer An instrument that measures air pressure Temperature A measure of how hot or cold an object is Troposphere Layer of the atmosphere nearest to Earth’s surface Stratosphere A clear, dry layer above the Troposphere Mesosphere Thermosphere The third layer which houses the thinnest air The hottest layer of the atmosphere Exosphere Outer space Ozone A gas made up of 3 oxygen atoms Nitrogen Cycle Water Cycle Ch. 1 &2 Concept Earth’s atmosphere makes life on Earth possible. Air becomes thinner as altitude increases The decrease of density with greater altitude means that most of the mass of the atmosphere is close to Earth’s surface. Carbon, nitrogen, & water are transferred into and out of the atmosphere. Continuous cycling of matter Continuous cycling of matter Continuous cycling of matter Air molecules move in all directions & air pressure pushes in all directions Measures the air pressure differences that set air in motion Air’s temperature changes with altitude Supports life: Water vapor Warmed by Earth Right amount of oxygen Contains the ozone layer to protect life from solar radiation The layer where meteors burn up So hot it feels cold to your skin because the molecules are so spread out Sometimes known as the 5th layer helpful or harmful depending on which layer it is located in