Molecular Geometry Notes
advertisement

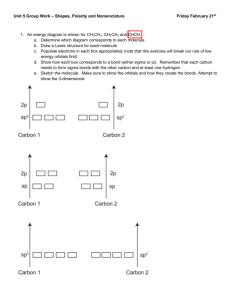
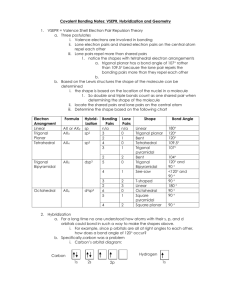
R-13 Molecular Geometry Notes VSEPR THEORY: _______________ _______________ between valence electrons surrounding an atom causes these electron pairs to be located as far apart as possible. V: _______________ S: _______________ E: _______________ P: _______________ R: _______________ VSEPR allows for the prediction of the ____________ _________ of molecules. Geometric shape is based on _______________ and _______________ pairs of electrons that are attached to the _______________ atom. Unshared pairs are __________ the same as bonded pairs; unshared pairs push a little harder! Five Basic Shapes of Molecules: 1. ________________________________________ 2. ________________________________________ 3. ________________________________________ 4. ________________________________________ 5. ________________________________________ Five basic shapes of molecules: Bond Angles Central Atom Examples 1) Tetrahedral 2) Trigonal pyramidal 3) Trigonal planar 4) Bent a. b. 5) Linear a. b. c. d. e. 2 Hybridization Valence electrons are found in _______________ and _______________ You would expect s to s bonds would be different than s to p bonds or p to p bonds, but they are not. _________________________________________ Hybridization- the _______________ of two or more orbitals of similar energies on the same atom to give __________orbitals of equal energy. Orbitals blend to form special orbitals for bonding. Blended orbitals are _____________. Hybridization explains how electrons can form identical bonds even though some are from the ________________ and some are from the ________________. ___ ___ ___ p ___ ___ ___ ___ sp3 hybridization ______ s Sigma and Pi Bonds Single covalent bonds are also called _________________________. Sigma bonds are formed when orbitals ______________ between the two sharing atoms (hybrid orbitals.) ____________________ are the additional bonds that form from overlapping p orbitals. They only form _______________a sigma bond is formed. single bond – _______________ double bond – ____________________ triple bond – ____________________ The number of hybrid orbitals is determined by the ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ _________________________ indicates which orbitals are occupied 3 ___ ___ ___ p ___ ___ ___ ___ sp3 hybridization ______ s Shape Generic Formula # of sigma bonds and unshared pairs Hybridization Tetrahedral Trigonal Pyramidal Trigonal Planar Bent Linear- when only two atoms, you must be told which one is considered the central atom 4 Polarity A polar molecule has _____ and _____ areas within it. Molecules _______ _______ be non-polar even if their bonds are polar: CO2. So how do you know? ________________________________________________________________________ If uneven (not identical) distribution, then molecule is __________. If even distribution (identical), then molecule is __________. Look only at the _______________ _______________ when determining polarity of a molecule. Unshared pairs are __________ the same as shared pairs. Examples ____________________ ____________________ ____________________ 5 Determining Polarity After drawing the Lewis structure and identifying the molecular shape, it is easy to determine the polarity of a molecule. After determining the shape, look at whether the atoms surrounding the CENTRAL atom are all identical to one another. Bent and trigonal pyramidal molecules are ALWAYS polar. Molecular Shape Linear Bent Trigonal planar Trigonal pyramidal Tetrahedral Is everything surrounding central atom identical? Molecular Polarity yes non-polar no polar - polar yes non-polar no polar - polar yes non-polar no polar 6