File
advertisement

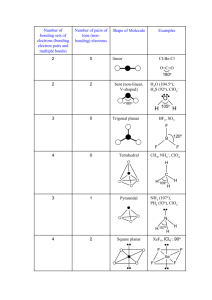
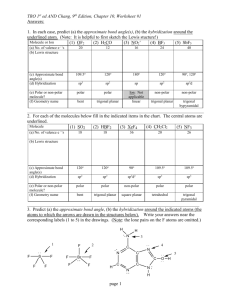
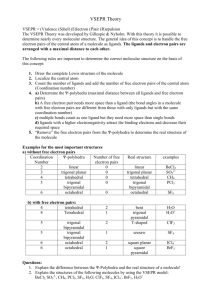
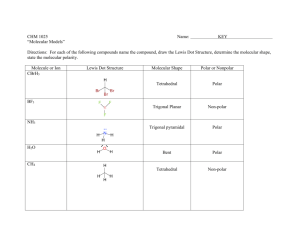
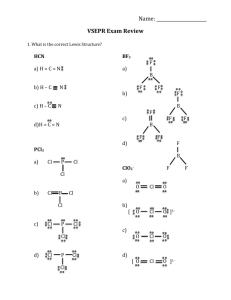
TUTORIAL #7 – Chemical Bonding II (with answers) 1. Fill in the table below with the correct answers: (Hint: First, draw the Lewis structures, then; use the structures as a guide to determine the electron pair and the geometry) Species Class No. of bonding pair electron No. of lone pair electron Arrangement of electron pairs Molecular geometry (shape) SeF6 IF3 TeF4 XeF5+ ClF2– XeO3 2. Iodine forms three compounds with chlorine: ICl, ICl3 and ICl5. Draw the Lewis structures and determine the molecular geometry (shape) of these molecules. 3. *Which of these molecules are polar? For each polar molecule, indicate the direction of the net dipole. (Clue: Draw Lewis structure first, then determine the molecular shape, check the surrounding atoms, be careful if there are more than two types of surrounding atoms! Check electronegativity!) (a) H2O (d) ClF (g) CH3Cl (b) NH3 (e) CCl4 (h) SO3 (c) CO2 (f) HBF2 4. *State the values of the indicated bond angles below. (a) O—S—O angle in SO2 (b) F—B—F angle in BF3 (c) (d) 1 5. Describe the hybridization around the central atom and the bonding in PF5. 6. *Acrylonitrile is polymerized to manufacture carpets and wigs. Its Lewis structure is as follows: (a) How many sigma (σ) bonds are in the molecule? (b) How many pi (π) bonds are in the molecule? (c) What is the hybridization of the carbon atom that is bonded to nitrogen? 7. *Draw the Lewis structures and designate which are sigma (σ) and pi (π) bonds in each of these molecules: (a) OCS (b) NH2OH (c) CH2CHCHO (d) CH3CH(OH)COOH 8. *Complete the table below: Compound Arrangement of electron pairs Molecular geometry (shape) Hybridization on central atom The bond angle on the central atom Polar or non-polar? PF3 XeCl4 NCl3 AsH3 BCl3 2 ANSWERS : 1. Class No. of bonding pair electron No. of lone pair electron Arrangement of electron pairs Molecular geometry (shape) AB6 6 0 Octahedral Octahedral IF3 AB3E2 3 2 Trigonal bipyramidal T-shaped TeF4 AB4E 4 1 Trigonal bypiramidal XeF5+ AB5E 5 1 Octahedral ClF2– AB2E3 2 3 Trigonal bypiramidal Linear XeO3 AB3E 3 1 Tetrahedral Trigonal pyramidal Species SeF6 2. Distorted tetrahedral (see-saw) Square pyramidal Answer: Linear T-shaped 3. Square pyramidal Answer: (a) polar (d) polar (g) polar (b) polar (e) non-polar (h) polar (c) non-polar (f) polar 4. (a) 120o (b) 120o (c) ∡1 = 120o , ∡2 = 180o (d) ∡1 = 109.5o , ∡2 = 120o 5. Answer: In PF5, there are 5 electron pairs around phosphorous, all bonding pairs. This requires 5 hybrid orbitals which can be produced by sp3d hybridization. The five P—F sigma bonds are formed by head-to-head overlap of the sp3d hybrid orbitals on P with 2p orbital on F. PF5 has an arrangement of trigonal bipyramidal and the shape is also trigonal bipyramidal. 3 6. (a) Six sigma (σ) bonds (b) Three pi (π) bonds (c) sp hybridization 7. 8. (a) (b) (c) (d) Complete the table below: Compound Arrangement of electron pairs PF3 Tetrahedral XeCl4 Octahedral NCl3 Tetrahedral AsH3 Tetrahedral BCl3 Trigonal planar Molecular geometry (shape) Trigonal pyramidal Square planar Trigonal pyramidal Trigonal pyramidal Trigonal planar The bond angle on the central atom Polar or non-polar? Sp 107.3o Polar sp3d2 90o Non-polar 3 107.3o Polar Sp 3 107.3o Polar sp2 120o Non-polar Hybridization on central atom 3 Sp 4