QUIZ 4 4 December 2008
advertisement

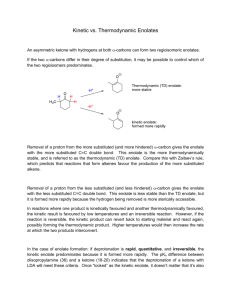
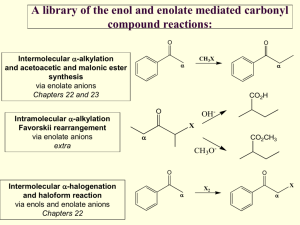
CH223 ORGANIC CHEMISTRY II QUIZ 4 4 December 2008 Time allowed: 80 minutes Attempt all 43 questions by writing answers for each question on the grid answer sheet provided 1. Why is an amide less reactive to nucleophilic acyl substitution 5. What is the first step in the general mechanism for nucleophilic than an acid chloride? acyl substitution? A. Nitrogen is a better leaving group. A. Protonation of the carbonyl B. Chloride is a better leaving group. B. Removal of an -proton C. Nitrogen is better at donating electron density into the C. Addition of the nucleophile to the carbonyl carbonyl with added resonance stability. D. Loss of the leaving group D. The amide anion is less basic. 6. 2. Why doesn't nucleophilic acyl substitution stop at the What would you see in the IR spectrum of a carboxylic acid? tetrahedral intermediate? A. A flat line (carboxylic acids are not IR active) A. The nucleophile is too basic. B. A sharp line at 2250 cm-1 B. Reforming the carbonyl is energetically favorable. C. A broad peak from 3800-2800 cm-1 C. The leaving group is unstable and wants to be negatively D. A broad peak from 800-600 cm-1 charged. D. There is no tetrahedral intermediate. 3. Where do the carbonyl signals appear in the 13C NMR spectrum of carboxylic acid derivatives? 7. A. 1700 cm-1 B. 180-160 ppm C. 2.5-3.0 ppm Why is pyridine included in the reaction of an acid chloride and an amine or alcohol? A. D. 100-80 ppm a better nucleophile. B. 4. Pyridine will deprotonate the amine or alcohol, making it Which structure is consistent with the following 1H NMR Pyridine will neutralize the acid by-product of the reaction. spectrum? C. Pyridine will protonate the carbonyl of the acid chloride, making it more reactive. D. Pyridine will absorb the heat of the reaction. 8. A. Ethyl acetate B. 2-propanone C. 3,3-dimethylpentanone What is the product of the following reaction? D. Ethyl 2,2-dimethylpropionate 1 9. What is the product of the following reaction? 14. 10. What is the direct product of the base-promoted hydrolysis of an ester? A. A nitrile B. A carboxylic acid C. An amide D. A carboxylate salt What reagent would you use for the following transformation? A. LiAlH4 B. DIBAL-H C. NaBH4 D. H2, Pd/C 15. What is the structure for the compound whose IUPAC name is pentyl 2-methylbutanoate? 11. Which of the following two amides will react more readily with a nucleophile? Why? A. A B. B C A. 1, because it is less hindered C. B. 2, because it is less hindered D. D C. 1, because it is more strained D. 2, because it is more strained 12. What is the product of the following reaction? 13. What is the product of the following reaction (after acidic 16. What is the product? work-up)? A. A B. B C. C D. D 2 17. What is the product? 21. Which of the following reaction conditions can be used to synthesize an ester (RCOOR')? 18. What is the product? A. RCOCl + R'OH + pyridine B. RCOOH + R'OH + H+ C. RCOOH + R'OH + OH- D. RCONH2 + R'OH E. Both RCOCl + R'OH + pyridine and RCOOH + R'OH + H+ are acceptable methods. 22. Which of the following substrates cannot be used as an immediate precursor to synthesize an ester? A. A A. A B. B B. B C. C C. C D. D D. D 23. From the list below, pick the compound that does not react with 19. What is the product? HO2C CO 2H acetyl chloride. A. Isopropyl alcohol B. Benzoic acid C. Ammonia D. Triethyl amine 20. What is the product? 3 24. Which of the statements below is true about amides? A. 27. Which is the more stable form of acetophenone? Amides react with methyl alcohol in the presence of an acid catalyst to form an ester. B. Amides are hydrolyzed in acid or base to form carboxylic acids or carboxylate anions. C. Amides react with thionyl chloride to form the acid chloride. D. Amides do not react under any conditions. They are inert compounds. A. A B. B C. C 25. n-Butanenitrile will undergo all of the following listed reactions except one. Which reaction listed is not true for n- 28. Why is the enolate of acetone less basic than the allyl anion butanenitrile? derived from propene? A. n-Butane nitrile will react with ethylmagnesium bromide A. Because there are more atoms in acetone to form an alcohol. B. Because there are more resonance structures for the B. C. n-Butanenitrile with be reduced to butyl amine in the enolate of acetone presence of LiAlH4 with a water work-up. C. n-Butanenitrile is hydrolyzed in the presence of acid to D. One of the resonance structures for the enolate places the form butanoic acid. It isn't (the allyl anion is less basic). charge on the more electronegative oxygen. D. n-Butanenitrile is reduced with DIBAL-H to form nbutanal. 29. Which of the following four compounds is the most acidic (i.e., has the lowest pKa value)? 26. An unknown compound has a sharp, medium peak at 2250 cm1. The unknown compound is probably A. an alkane. B. an aldehyde. C. an alkene. D. a nitrile compound. A. A B. B C. C D. D 4 30. Which is the kinetic enolate of 2-methylcyclohexanone? 34. Why is it difficult to stop the halogenation of ketones under basic conditions at the mono-halogenated stage? A. The ketone undergoes a Bayer-Villigar oxidation. B. The ketone is reduced. C. The ketone undergoes an Aldol reaction. D. The bromine helps to stabilize the second enolate, making the product more acidic than the starting material. 35. Starting with cyclohexanone, how could you prepare the A. A B. B C. C diketone below? D. D 31. If you want to form a thermodynamic enolate, you want to A. Treat cyclohexanone with a base under thermodynamic conditions. A. keep the reaction as cold as possible. B. Hydrogenate cyclohexanone with Raney nickel. B. use an aprotic solvent such as THF. C. Convert cyclohexanone into the -bromoketone and then C. use a protic solvent such as ethanol. react this with the enolate of cyclohexanone. D. use a carboxylic acid. D. Convert cyclohexanone into an enamine with diethylamine and then react this with more cyclohexanone. 32. If you want to form a kinetic enolate, you want to A. use a strong, non-nucleophilic base such as LDA. B. use a protic solvent. C. use a low temperature. 36. What is the product of the following reaction? 37. What is the product of the following reaction? 38. What is (are) the product(s) of the following reaction? D. both use a strong, non-nucleophilic base such as LDA and use a low temperature. E. both use a strong, non-nucleophilic base such as LDA and use a protic solvent. F. both use a protic solvent and use a low temperature. 33. What is the intermediate for halogenation of ketones under acidic conditions? A. An enolate B. An enol C. A tautomer D. An epimer 5 39. Which of the following are enol forms of ethyl acetoacetate? 42. The reaction below is a direct enolate alkylation. It has been found that this reaction only works well with unhindered methyl and 1 alkyl halides. Pick the statement that best explains this observation. A. A A. The nucleophilic enolate requires a reaction center that B. B C. C B. Hindered alkyl halides do not undergo SN1 reactions. D. D C. Hindered alkyl halides do not undergo SN2 reactions. has a positive charge. D. Methyl and 1 alkyl halides can form carbocations that can 40. For most compounds with a single keto group in the molecule, readily react with the nucleophilic enolate. equilibrium favors the keto form over the enol form of the compound. This is due largely to 43. A simple chemical test to distinguish between acetone and 3pentanone would be the reaction of the compounds with A. the C O bond is much stronger than the C C bond. B. the C C bond is much stronger than the C O bond. A. bromine with acetic acid. C. the keto form can always form intramolecular hydrogen B. bromine and aqueous hydroxide ion. bonding. C. THF, LDA at -78 C followed by the reaction with D. the enol form can always form intramolecular hydrogen bonding. bromine. D. base and methyl bromide. 41. It has been found that -dicarbonyl compounds have a greater concentration of the enol form over the keto form. This can be explained by: A. the C C of the enol is conjugated with the carbonyl group. B. the -OH of the enol can hydrogen bond to the oxygen of the nearby carbonyl group. C. both of these answers are true. D. none of the choices are true. 6 CH223 QUIZ 4 ANSWER GRID Name……………………….. 1(1점) Student Number……………………… 2(1점) 3(1점) C 6(1점) C 4(1점) B 7(1점) D 8(2점) B B NHEt HO 12(2점) 13(2점) C 16(1점) NH2 17(2점) D O N H 15(1점) B O A 19(2점) A CO2H 10(1점) 14(1점) 18(1점) C C 9(2점) O 11(1점) 5(1점) O 20(2점) O O O OMe 21(1점) 22(1점) E 26(1점) 23(1점) B D 27(1점) D 31(1점) 28(1점) B 36(4점) OH C 35(1점) D 39(1점) O O 30(1점) 34(1점) 38(2점) A C B 37(4점) O 29(1점) 33(1점) D 25(1점) B D 32(1점) C 24(1점) C 40(1점) D A + CHI3 O 41(1점) 42(1점) C 43(1점) C Total Score B 60 (기본점수 3점) 7