Chemistry 125: Lecture 70
April 19, 2010
Acyl Compounds
(Ch. 18)
-H Reactivity
This
(Ch. 19)
For copyright
notice see final
page of this file
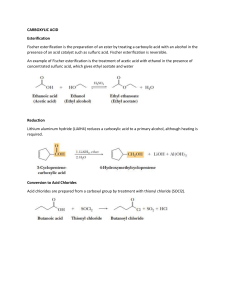
Fischer Esterification
(sec. 17.7a)
+
starts with
+
addition O
H
+ substitution
R C
OR
O
H
+
RO
H
Tetrahedral Intermediate
at C
(A/D, not pentavalent transition state)
Victor Meyer
(1848 - 1897)
Victor Meyer 9/8/48 - 8/8/97
“Geliebte Frau! Geliebte Kinder!
Lebt wohl! Meine Nerven sind
zerstört; ich kann nicht mehr.”
introduced
the idea of
Steric
Hindrance
(1894)
“…the source of this behavior
is stereochemical…the space
filling of the neighboring groups”
Configuration van’t Hoff (1874)
Conformation
Sachse (1891)
Fischer Esterification Didn’t Work
with 2,6-Dimethylbenzoic Acid
Carboxylic Acid
Tetrahedral Intermediate
STRAIN!
Melvin
Newman’s
Method
Fischer
Esterification
(sec. 20.8, p. (1941)
965)
Linear
Tetrahedral
Acylium
Intermediate
Intermediate
(D/A,(A/D)
like SN1)
+
+
H
O
+
R C +O
O HH+
+ OR
+
+
Pour into ROH HH
OH
100% H SO
H
R
substitution
at C
(attaching second H+
inhibits reversal)
sometimes
2
4
Acyl Derivatives from Ketene
sec. 18.11, p. 907
H2C=C=O
Nu:
Baeyer-Villiger Reaction (insert O)
pp. 907-909
Remember PhCHO + O2
H- migration
R- migration
Migration from Acyl Carbon
+
R C
O
inserts X
between
R and C=O
X L
R
Beckmann Rearrangement (insert N)
pp. 909-911
inserts in
anti bond
Beckmann Rearrangement (insert N)
pp. 909-911
R- migration
in cation
Arndt-Eistert Reaction (insert C)
pp. 915-917
Wolff
elongates acid by one carbon
Rearrangement R- migration
Acidity
Tables 19.1 (p. 933), 19.2 (p. 943), 19.3 (p. 958)
H
pKa ~ 18
LDA hindered strong base (pKa = 36)
(p. 944)
pKa ~ 25
K ~ 1011
complete formation of enolate
not just a little at equilibrium
(slow attack on C=O, none on enolate)
Acid & Base H/D Exchange
via enol and enolate
(sec. 19.2a)
Racemization via enol and enolate
(sec. 19.3)
-Halogenation
ketones/aldehydes (19.4a)
Iodoform with base
+
-Halogenation
carboxylic acids (19.4b)
Hell-Volhard-Zelinsky
End of Lecture 70
April 19, 2010
Copyright © J. M. McBride 2010. Some rights reserved. Except for cited third-party materials, and those used by visiting
speakers, all content is licensed under a Creative Commons License (Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0).
Use of this content constitutes your acceptance of the noted license and the terms and conditions of use.
Materials from Wikimedia Commons are denoted by the symbol
.
Third party materials may be subject to additional intellectual property notices, information, or restrictions.
The following attribution may be used when reusing material that is not identified as third-party content:
J. M. McBride, Chem 125. License: Creative Commons BY-NC-SA 3.0